Distributed System II
越写越慢。敬佩小土刀前辈。这一篇关于分布式系统下的通信和RPC。
首先Daniel介绍了网络相关知识和一些需要知道的概念👇 …他真可爱,可…

Communication
这节主要介绍相关概念。首先介绍了一些Communication的常见概念:
Multiplexing 多路复用: share network resources
Packet Switching 分组交换: Source sends independent information as self-contained packets that have an address.
Packey Delay 包延迟:
- Sum of a number of different delay components:
- Propagation delay on each link.
- Proportional to the length of the link
- Transmission delay on each link.
- Proportional to the packet size and 1/link speed
- Processing delay on each router.
- Depends on the speed of the router
- Queuing delay on each router.
- Depends on the traffic load and queue size
Commication channel model:
- Latency - how long does it take for the first bit to reach destination
- Capacity - how many bits/sec can we push through? (“bandwidth”)
- Jitter - how much variation in latency?
- Loss / Reliability - can the channel drop packets?
-
Reordering
Stop & Forward: 2*(Prob + xmit)
Cut through: 2*Prob + xmit Stop & Wait: sender wait for ack before next communication
….DS出分了我考的是个什么ಥ_ಥ 我不配崇拜Daniel不配喜欢w腿。我还继续写吗,反正又不会有什么用。我这一学期只努力学习DS,只有DS崩了。是我学的还不够努力,一定是这样…. 心痛到不能呼吸:) 这大概,就是弱吧…
Internet
- An inter-net: a network of networks
- The Internet: the interconnected set of networks of the Internet Service Providers
- Challenges:
- Heterogeneity: address format/performance/packet size/routing/loss/in-order delivery
- Standard -> IP
IP Layering
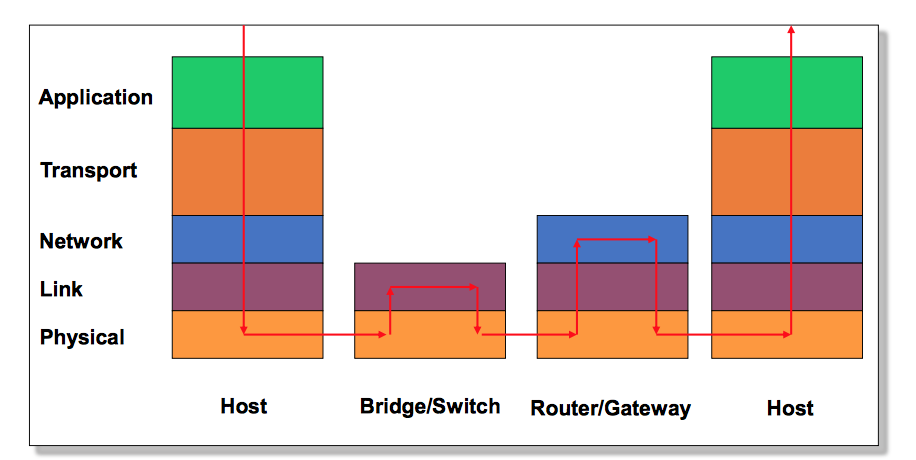
…和之前通信学的是一样的。
Failure models
- Fail-stop: When something goes wrong, the process stops / crashes / etc
- Fail-slow/fail-stutter: Performance may vary on failures as well
- Byzantine: Anything that can go wrong, will. 我考试一定是基于拜占庭模型的考试…
Client & Server
- Client: Initiates contact with server/Typically requests service from server
- Server: Provides requested service toclient
TCP VS. UDP
| TCP | UDP |
|---|---|
| Reliable - guarantee delivery | Unreliable ☺, no guarantee of delivery |
| Byte stream – in-order delivery | Single socket to receive messages - not necessary in-order |
| Connection oriented - single socket/connectoin | Datagram – independent packets, must address each one |
| One round-trip time to setup connection/fix lost packet | Packet sliently disappears |
| Figures out how fast to send data | No |
| e.g. Phone call, web, email, telnet | e.g. postal mail, multimedia, voice over IP |
Remote Procedure Calls
RPC,远程过程调用,试图将远程调用表现的如同本地的调用。 RPC goals:
- Ease of programming
- Hide complexity
- Automates task of implementing distributed
computation
- Familiar model for programmers
RPC可以使远程的调用看起来像本地调用,因此提供了分布式的透明性,但是由于在不同的机器上调用,可能有不同的地址空间和OS,要将数据转换为本地的格式。
Client Stub:
- Marshals arguments into machine-independent format
- Sends request to server
- Waits for response
- Unmarshals result and returns to caller
Server stub:
- Unmarshals arguments and builds stack frame
- Calls procedure
- Server stub marshals results and sends reply
所以,值传参会比地址传参简单得多。值传参只需要将值复制到network中,而地址传参需要事先知道数据的大小,发送一份数据的拷贝,放在远程系统的内存中,讲这块地址的指针传到server,然后发送给client。
RPC Failures
Partial: local computing/distributedcomputing
Solution: Strawman
Possible semantics
- Exactly once: impossible in practice
- At least once: only for idempotent operations, client try until success
- At most once: 0 or 1, client give up easily
- Zero or once: same as at most once
自我怀疑,不是重点的东西不写了。