Distributed System V
“Hi everyone, welcome back to Distributed System \(//∇//)\ Today we will talk about Fault Tolerance in Distributed System…” Daniel常用开场白。
这一篇主要关于分布式系统下的容错,介绍了比如Checkpoint,Logging & Recovery,Replication等和RAID。这一部分在DS中要求重点掌握PAXOS。可惜没有PAXOS这个prj, RAFT也还行吧唔。
Logging and Recovery
这一部分Daniel讲了, 分布式系统下的容错机制。在出现部分错误的情况下,系统应该是可靠的。如何定义可靠呢?emmm, 颜即正义,呸 (Availability, Reliability, Safely, Maintainability)
Dependability Concepts
Availability 可用性: the system is ready to be used immediately
Reliability 可靠性: the system runs continuously without failure
Availiability 和 Reliability 也是tradeoff. 比如一个低MTTF的系统,就会有低可用性,因为它具有高可靠性。
Safety 安全性: if a system fails, nothing catastrophic will happen
Maintainability (Recovery) 可维护性: when a system fails, it can be repaired easily and quickly
Failure Models
Crash/Omission/Timing/Response/Arbitrary(Byzantine)
Redundancy
Information Redundancy: add extra bits to allow for error detection/recovery
Time Redundancy: perform operation and, if needs be, perform it again.
Physical Redundancy: add extra (duplicate) hardware and/or software to the system
Checkpoint
Backward recovery: return the system to some previous correct state (using checkpoints), then continue executing (Common one)
- Checkpointing can be very expensive (especially when errors are very rare)
Forward recovery: bring the system into a correct new state, from which it can then continue to execute
-
Harder to know howdo to bring the system forward to a correct state.
如果failure发生,系统可以通过Checkpoint恢复到一个较早的状态。在多线程背景下Checkpoint出现多线程Transaction,这个Checkpoint就是inconsistent的。所以出现了Coordinated Checkpointing这个概念。
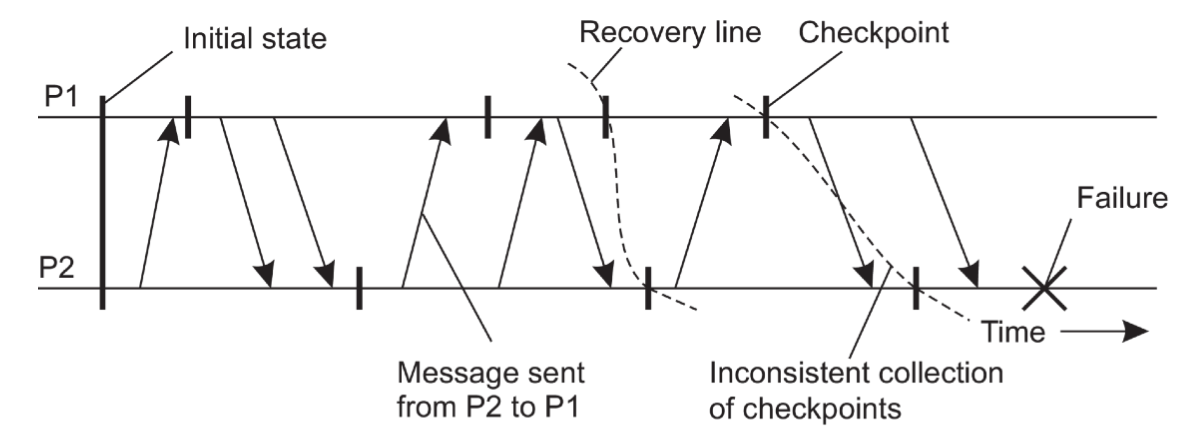
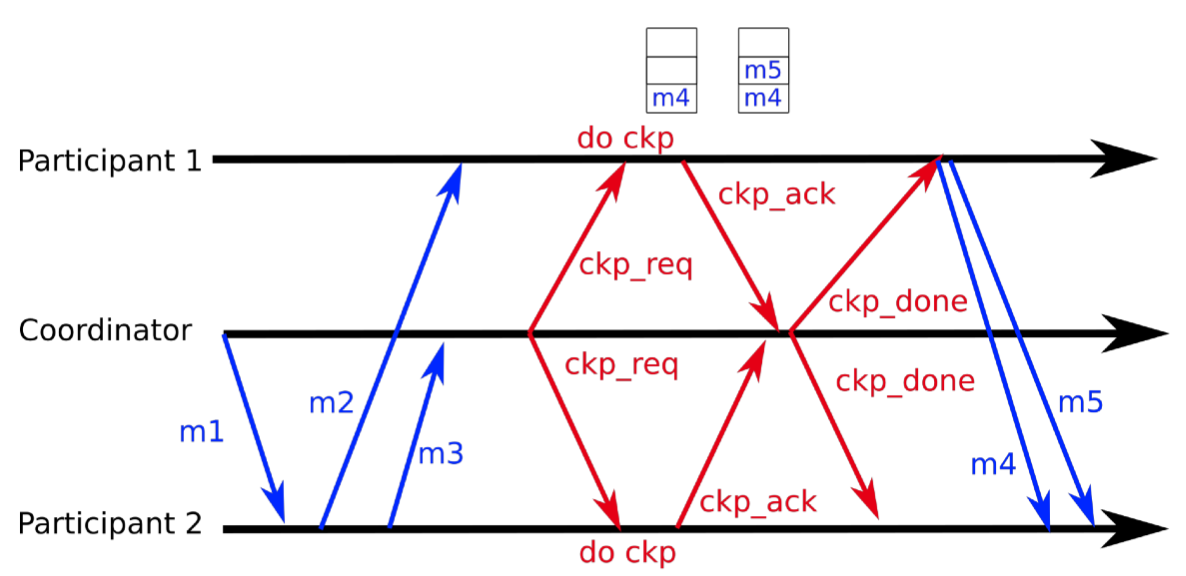
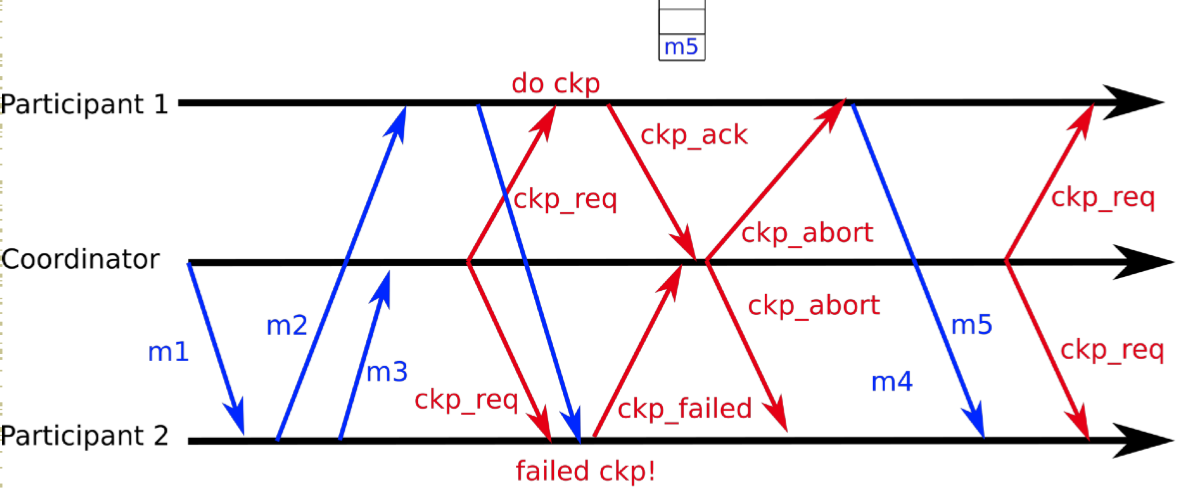
Coordinated Checkpointing
Key idea: each process takes a checkpoint after a globallycoordinated action
Simple Solution: 2-phase blocking protocol
Optimization: consider only processes that depend on therecovery of the coordinator
| Successful Coord | Unsuccessful Coord |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Logging and Recovery
Goal: make transaction reliable.
General idea: store enough information to disk to determine global state
Challenges: disk performance is poor, writing to disk to handle arbitrary crash is hard -> Shadow pages and Write-ahead Logging (WAL), providing Atomicity and Durability
Shadow Paging Vs WAL
| WAL | Shadow Page | |
|---|---|---|
| ACID | A, D | A, D. page = unit of storage |
| Idea | create log recording every update to db | When write a page, make a shadow copy |
| ABORT | recover by replaying log | discard shadow page |
| COMMIT | LOG typically store both REDO and UNDO | make shadow page real |
| Other | Update versions kept in memory | “copy-on-write” to avoid in-place page update |
- WAL is more common, fewer disk operations, transactions considered committed once log written.
ARIES
ARIES: Algorithms for Recovery and Isolation Exploiting Semantics
Principles
- Write-ahead logging
- Repeating history during Redo
- Logging changes during Undo
Write-Ahead Logging
- Pages on disk, some also in memory (page cache)
- “Dirty pages”: page in memory differs from one on disk
- Reconstruct global consistent state using
- Log files + disk contents + (page cache)
一条LOG包含很多信息: LSN: [prevLSN, TID, “update”, pageID, new value, ol value]
LSN: Log-Sequence Number, in order
TID, prevLSN: PrevLSN forms a backward chain of operations for each TID
TT: Transaction Table, all TXNS not written to disk
DPT: Dirty Page Table, all dirty pages in memory
Recovery using WAL
Analysis Pass
- Reconstruct TT and DPT (from start or last checkpoint)
- Get copies of all pages at the start
Recovery Pass (redo pass)
- Replay log forward, make updates to all dirty pages
- Bring everything to a state at the time of the crash
Undo Pass
- Replay log file backward, revert any changes made by transactions that had not committed (use PrevLSN)
- For each write Compensation Log Record (CLR)
- Once reach entry without PrevLSNdone
利用WAL来进行修复,首先是分析,在这一步中还原DPT和TT到crash的状态。通过浏览log文件从开始到Cheakpoint的部分,将所有的事务加到TT中,在TT中保持TID和LastLSN,找到REDO的开始。同时将进行了改动的page加入到DPT中,在DPT中保持pageID和recoveryLSN。在TT中LastLSN记录最新的改动,DPT中recoveryLSN记录的是最初的改动。
Redo过程中,通过检查DPT和log文件,可以找到所有没有commit到disk的事务。已经成功添加到硬盘的改动是不需要Redo的。Redo的过程同样修改TT,并且保证每个Transaction不会被处理两次。
在Redo过程中,当前的状态已经被更改为出现错误时的状态。Undo过程将当前没有Commit的Transaction恢复。可以看作是Backward recovery的过程。在TT中利用LastLSN,对于每个record恢复改动并且同时增加新的log文件。
顺便说WAL是可以和2PC搭配使用的。
Distributed Replication
这节讲容错技术中的拷贝。之前讲的Recovery技术由于等待时间长,所以在出现错误的时候为了保持系统的运行,拷贝是必要的。
Goal: Stay up during failures
对于拷贝,read-only的数据是很容易的,只需要拷贝很多就可以了。但是read-write的数据还涉及到一致性的问题。说到一致性…
Consistency
Strict Consistency
- Read always returns value from latest write
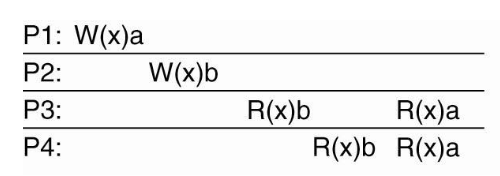
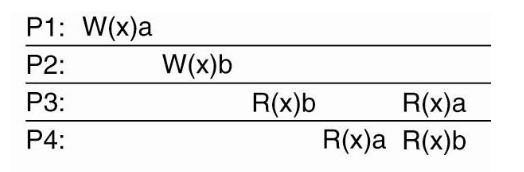
Sequential Consistency
- All nodes see operations in some sequential order
- Operations of each process appear in-order in this sequence
| Sequential Consistency | Violate Sequential Consistency |
|---|---|
 |
 |
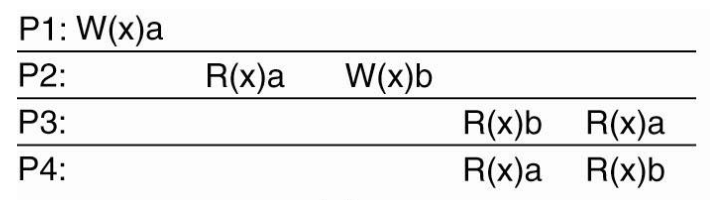
Causal Consistency
- All nodes see causally related writes in same order
- But concurrent writes may be seen in different order on different machines
| Causal Consistency | Violate Causal Consistency |
|---|---|
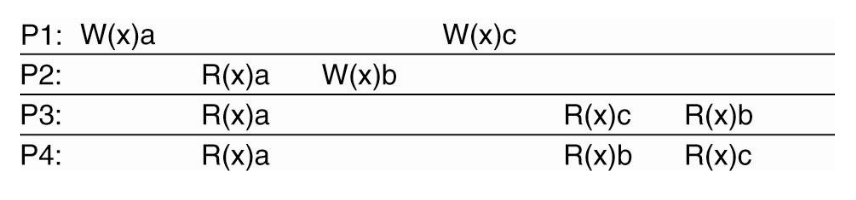 |
 |
Eventual Consistency
- All nodes will learn eventually about all writes, in the absence of update
Replication Strategies
- Propagate only a notification of an update
- Transfer data from one copy to another
- Propagate the update operation to other copies
When to replicate
Pull based: Replicas/Clients poll for updates (caches)
Push based: Server pushes updates (stateful)
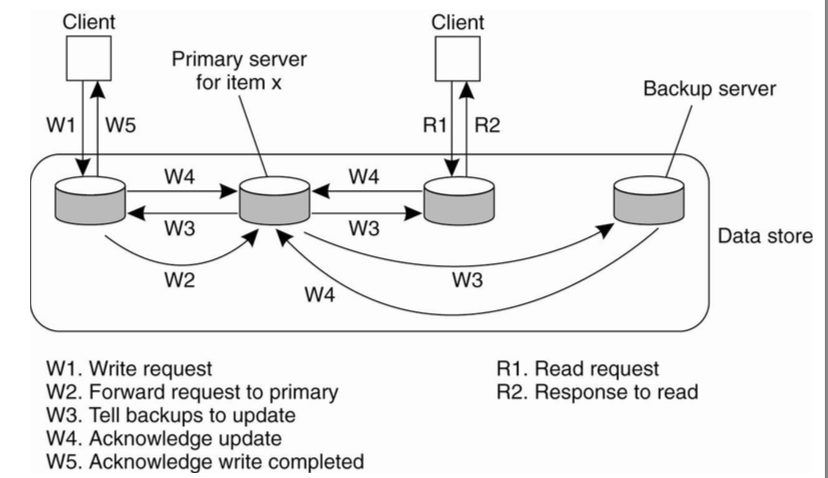
Primary-backup replication model
Assumptions
- Group membership manager
- Fail-stop(not Byzantine) failure model
- Failure detector
Primary-Backup Write Protocol
| Remote | Local |
|---|---|
 |
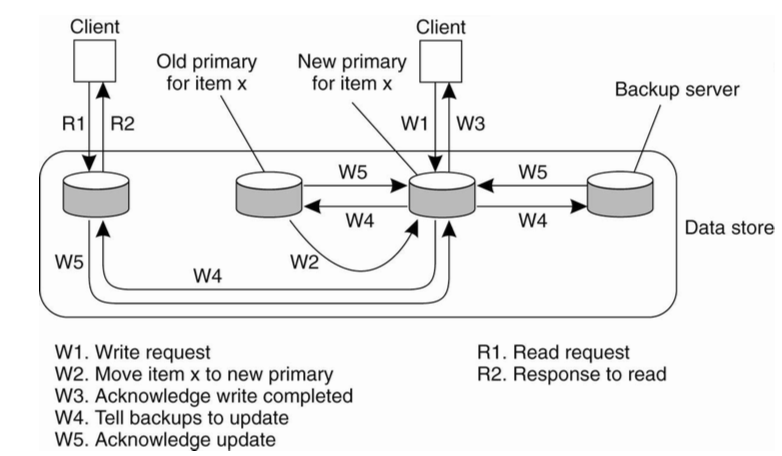 |
- Advantages: With N servers, can tolerate loss of N-1 copies
- Must wait for failure detector
Quorum Based Consensus
重点PAXOS
- Designed to have fast response time even under failures
- Operate as long as majority of machines is still alive
- To handle f failures, must have 2f + 1 replicas
- For replicated-write => write to all replica’s not just one
PAXOS
Components
- Proposers:
- Active: put forth particular values to be chosen
- Handle client requests
- Acceptors:
- Passive: respond to messages from proposers
- Responses represent votes that form consensus
- Store chosen value, state of the decision process
Single Decree Paxos
- Phase 1: Prepare message
- Find out about any chosen values
- Block older proposals that have not yet completed
- Phase 2: Accept message
- Ask acceptors to accept a specific value
- (Phase 3): Proposer decides
- If majority again: chosen value, commit.
- If no majority: delay and restart Paxos
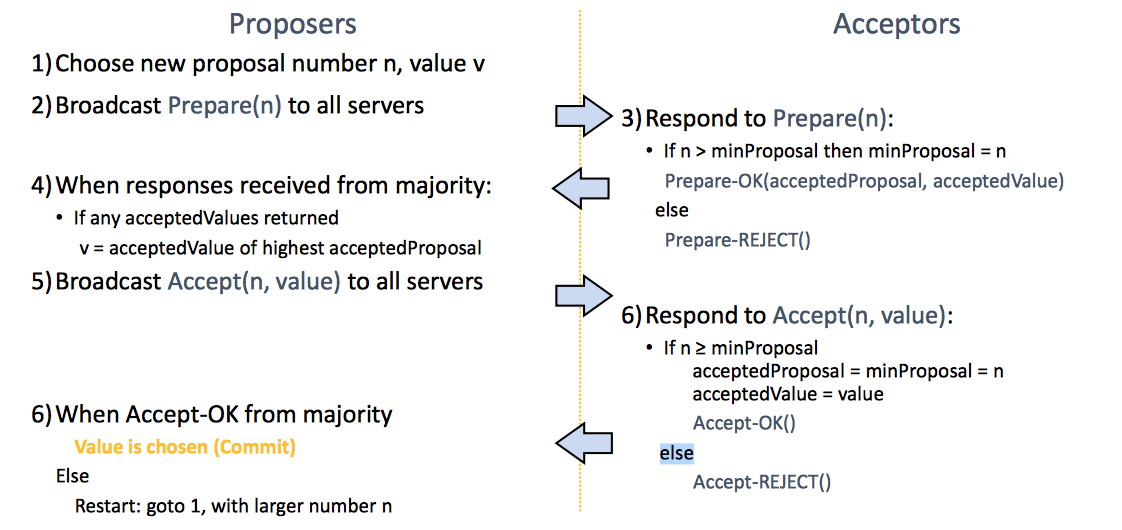
Paxos是非常重要的一个Protocal, 在工业界也有很广泛的应用。除了Single-Paxos, 还有Multi-Paxos但是没有重点介绍。
总之这一节主要介绍了Primary-backup和Quorum consensus两种拷贝的方式。其中Paxos是重点,在后半期DS的学习中也会有所应用。
| Primary-backup | Quorum consensus |
|---|---|
| Replicas are “passive”, follow primary | Replicas are “active”, participate in protocol, no master |
| Simple. N machines, can handle N-1 failures | Complex. To handle f failures, need 2f+1 replicas |
| Slow responses times in case of failures | Clients don’t see the failures |
Errors and RAID
这一节主要介绍了磁盘冗余阵列RAID,以及评估系统可用性的MTTF计算。
Type of Errors
Hard errors: Component is dead
Soft errors: A signal or bit is wrong, but doesn’t mean component is faulty
Meausuring Availability
**Availability = MTBF/(MTBF + MTTR) **
MTBF: Mean Time Between Failure
MTTR: Mean Time To Repair
MTTF: Mean Time To Failure
MTBF = MTTF + MTTR
Error Detection
介绍发现错误的一些方法。
Parity Checking
奇偶校验,之前学通信也接触过好几次。能够检测奇数次bit错误的发生,无法定位错误位置。
Block Error Detection
并不是所有的错误都能被探测。
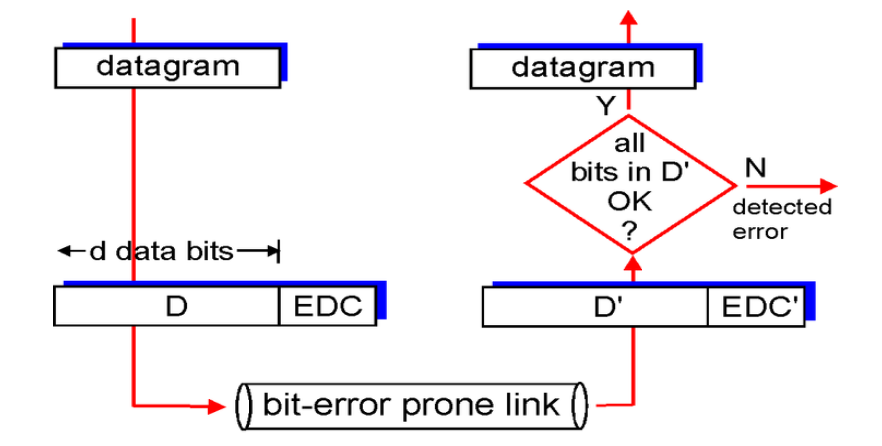
EDC: Error Detection Code
CheckSum
检查packet内所有的words/shorts/bytes的和。应用广泛,实现简单,很弱,许多诸如bit交换这种错误就无法检测…
Cyclic Redundancy Check
循环冗余检查,对于d比特的数据D,选择r+1比特的G,计算r比特的CRC添加到D后,得到数据<D, R>。<D, R>可以被G整除。发送<D, R>, 如果接收端无法整除G, 证明出现了错误。其中G是事先由发送和接收方达成一致的。可以检测出小于r+1比特的错误。
举个例子, D = 101110, G = 1001, r = 3. R = reminder[(D«<3)/G] = 011. 发送<D, R> = 101110011.
Error Recovery
检测出错误之后是错误的恢复。主要分两种情况,一种是利用冗余恢复,另一种是重新尝试直到成功。
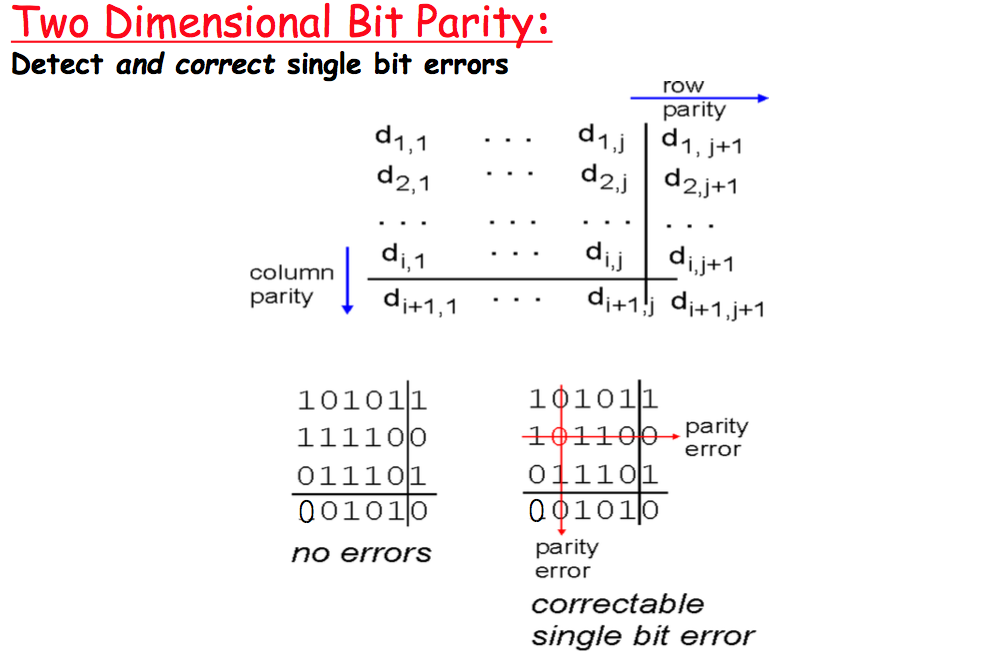
Error Correcting Codes
举个用奇偶校验码恢复错误的🌰,只能正确恢复1bit错误。
Replication & Voting
所有拷贝投票,选择majority。好像很不可靠的样子,因此一般在需要高可用性的系统中使用。
Retry
重新发一遍得到ACK,需要错误检测机制。
Fault Tolerance Design
如何将错误扼杀在摇篮里。
背景:Use multiple disks
- Capacity
- More disks allows us to store more data
- Performance
- Access multiple disks in parallel
- Each disk can be working on independent read or write
- Overlap seek and rotational positioning time for all
- Reliability
- Recover from disk (or single sector) failures
- Will need to store multiple copies of data to recover
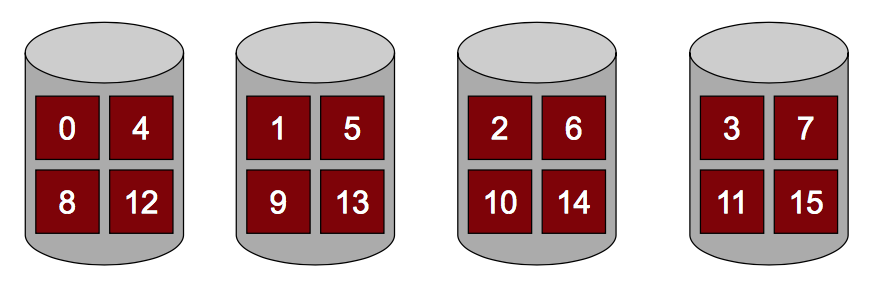
Disk Striping 硬盘分割: Interleave data across multiple disks
- Large file streaming can enjoy parallel transfers
-
Small requests benefit from load balancing
把数据交错的存在不同的硬盘上,可以并行的访问数据,并且可以保证数据流平衡。
JBOD
Just a bunch of disks. 就是一大堆硬盘?名字不错…
一大堆硬盘,每个硬盘之间没有关系,如果出现了错误无法恢复。
为了数据的安全,需要必要的冗余来进行备份和检测/修复错误。比较常见的数据冗余包括:replication 拷贝/ erasure-correcting codes 错误移除代码/ error-detecting codes 错误检测代码。对于拷贝,写操作写入所有的拷贝,读操作从任意一个读取。
Parity Disk
一个硬盘用来存所有的奇偶校验码,自检测。
Capacity: one extra disk save per stripe Erasures: disk failures aer self-identifying
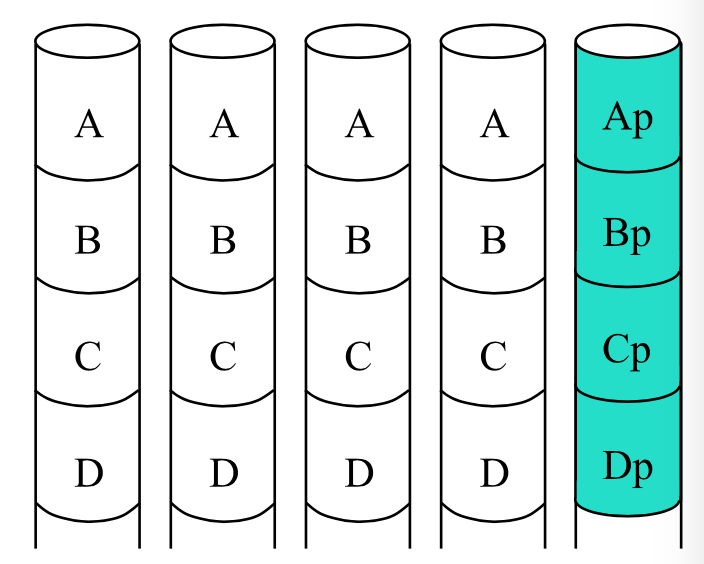
对于奇偶校验码和拷贝的存在,数据的无错误读操作可以并行读取,写操作要更新奇偶校验码。可以忍受一个错误。由于需要多次读/写奇偶校验码的硬盘,load balanced不存在的,会成为bottleneck。解决方式就是将奇偶校验码平均的分布到每一个硬盘上。
Striping Parity
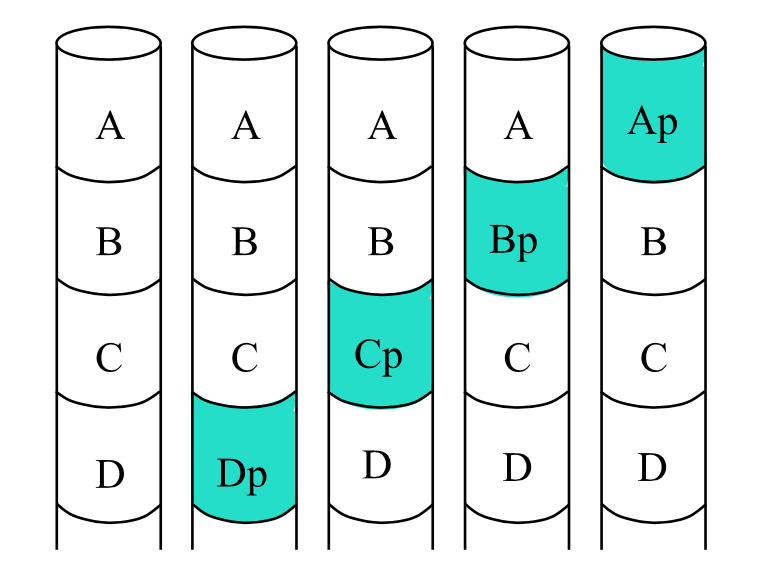
RAID
主要介绍RAID0, 1, 4, 5.
| RAID0: Striping | RAID1: Mirroring | RAID4: Parity | RAID5: Rotated Prity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance*4, Capacity*4, Reliability*1/4, Survive*0 | Performance:R*2 W<1, Capacity*2, Survive*1 | 4 I/Os per Write, Performance: R*3 W<1, Capacity*3, Survive*1 | 4 I/Os per Write, Performance: R*3 W<1, Capacity*3, Survive*1 |
 |
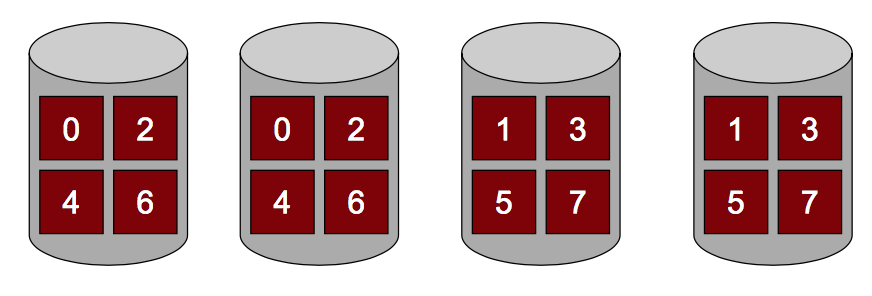 |
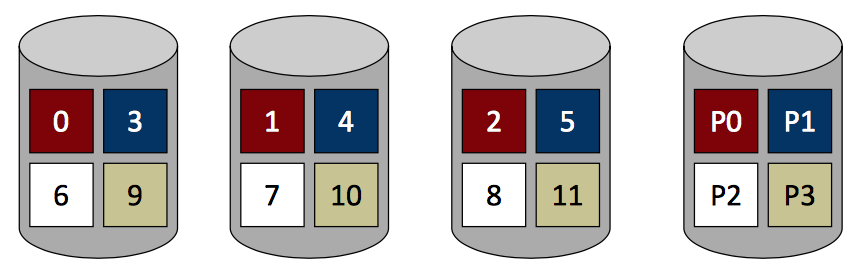 |
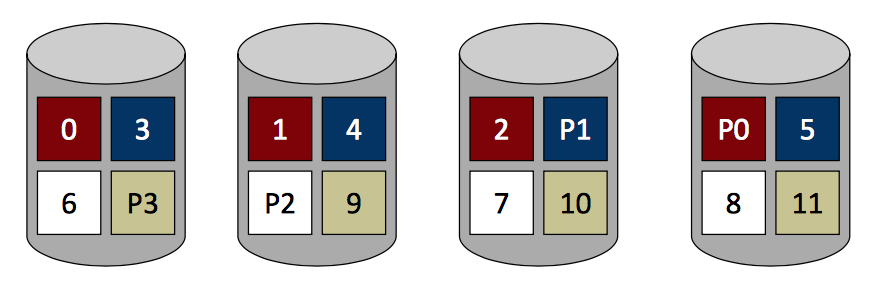 |
| Performance and capacity really matter but reliability doesn’t | Reliability and write performance matter, but capacity doesn’t | When capacity and cost matter or workload is read-mostly |
Compare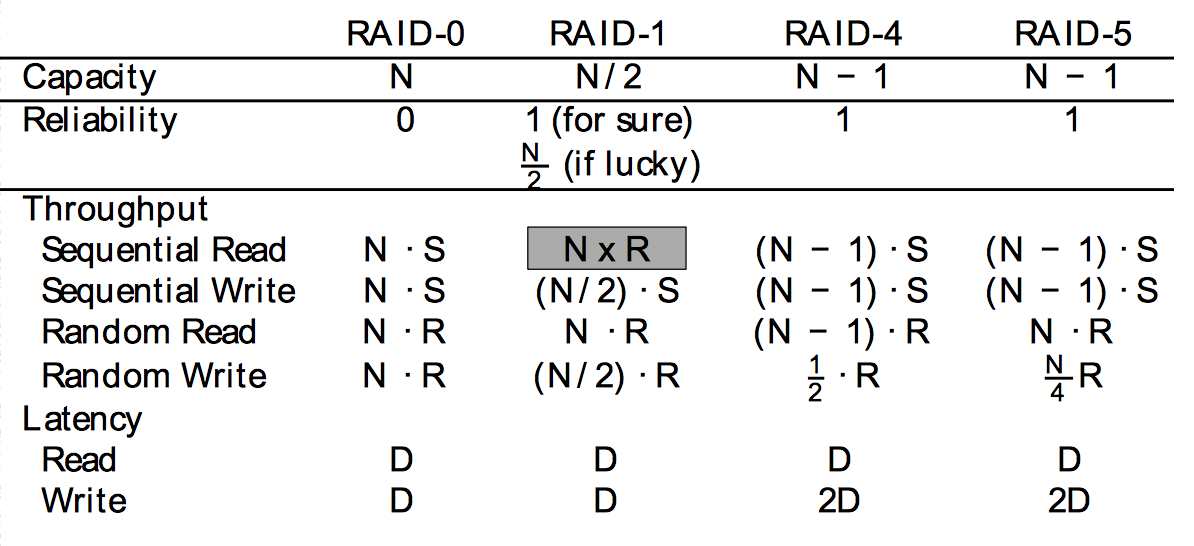
Availability/Reliability Metrics
可靠性/可用性相关计算,计算MTTDL(Mean Time To First Data Loss),本节的计算都是估算。
MTTF = mean time between failures (for each disk)
MTTDL = mean time to first disk failure (for each system)
MTTDL越大,可靠性越高,可用性越低。
Reliability without rebuild
Strip情况,系统的MTTDL = 硬盘MTTF/ 硬盘总数。
Mirror情况,系统MTTDL = 1.5*硬盘MTTF。
举几个🌰如下。
- 200 data drives with MTTF drive: MTTDLarray = MTTFdrive / 200
- Add 200 drives and do mirroring
- MTTFpair = (MTTFdrive / 2) + MTTFdrive = 1.5 * MTTFdrive
- MTTDLarray = MTTFpair / 200 = MTTFdrive / 133
- Add 50 drives, each with parity across 4 data disks
- MTTFset = (MTTFdrive / 5) + (MTTFdrive / 4) = 0.45 * MTTFdrive
- MTTDLarray = MTTFset / 50 = MTTFdrive / 111
Reliability with rebuild
奇偶校验码和镜像分别可以容忍一个错误。对于镜像,从正确的拷贝读取数据。对于奇偶校验码,已知错误硬盘,可以利用校验码XOR其他硬盘数据推断出正确比特。需要满足在没有数据丢失和在第二个错误发生之前修复第一个错误。
- MTTDLarray = MTTFfirstdrive * (1 / prob of 2nd failure before repair)
- prob is MTTRdrive / MTTFseconddrive
- Mirroring: MTTDLpair = (MTTFdrive / 2) * (MTTFdrive / MTTRdrive)
- 5-disk parity-protected arrays: MTTDLset = (MTTFdrive / 5) * ((MTTFdrive / 4 )/ MTTRdrive)
参考资料:Markdown的格式太丑了能改行间距吗好像不能用html+css也太麻烦了我就是想写个笔记而已啊
忍不住每一篇都表白Daniel但是一想到又不能跟他工作简直(;´༎ຶД༎ຶ`) 到这里为止期中考试之前的部分就结束了。如果足够厉害DS能A的话就可以申请和Daniel实验室打工了吧 这届DS不到92+不可能A 不愧是CMU 技不如人甘拜下风再见Daniel