Distributed System VIII
现在PIT飞往DEN的✈️。Daniel🎄要飞回🇩🇪,觉得偶遇机会为0,果然机场没遇到Daniel好可惜啊。这一篇主要关于谷歌和Hadoop的文件系统案例学习,GFS/HDFS。以及谷歌Database,Spanner。从来不晕机的我好像有点晕机,糟糕(;´༎ຶД༎ຶ`)
GFS/HDFS
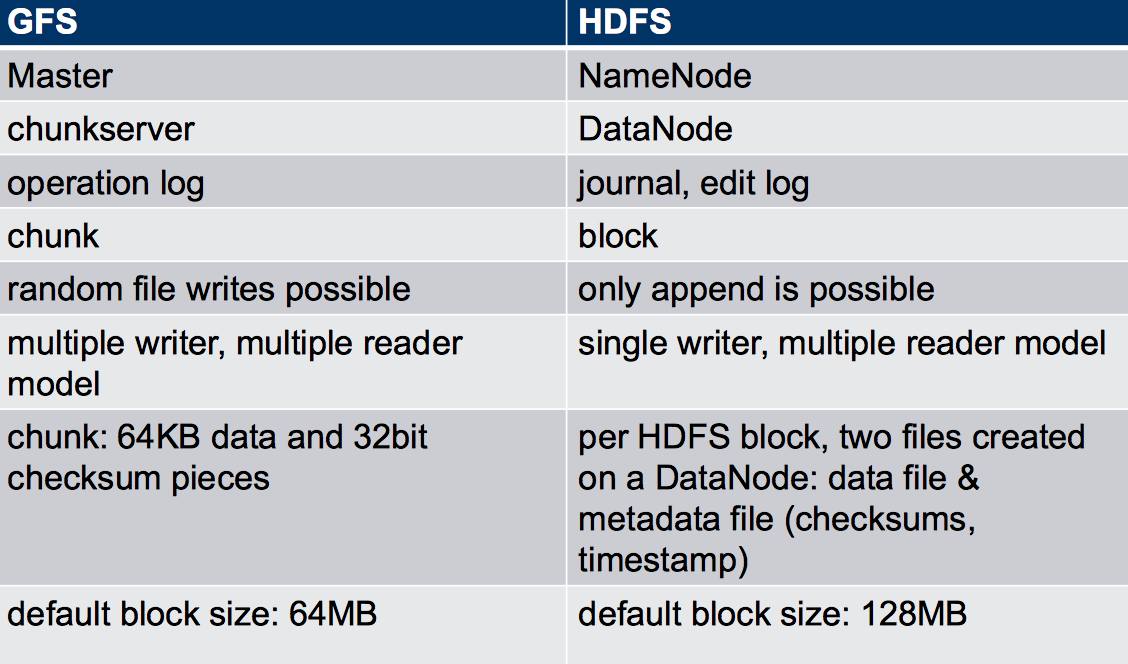
Google file system和Hadoop file system的结构很相似,都是将文件分成blocks分别存在chunk结构中,根据master中存储的metadata来进行访问。
GFS
GFS is a distributed fault-tolerant file system.
Assumption: large files/large sequential writes and append/large streaming reads/concurrent appends by multiple clients
GFS的重点在于理解GFS的结构和读写操作模型,其他的倒也没什么…
GFS Architecture
- One master server
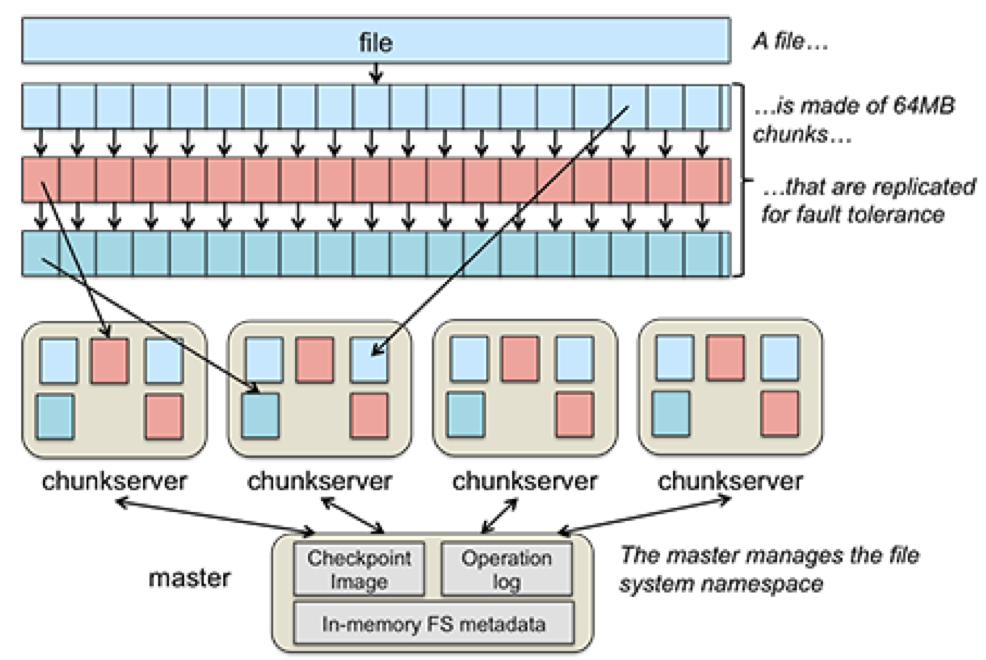
- Many chunk servers: 64MB portion of file, identified by global ids
- Many clients accessing same/different files stored on same cluster
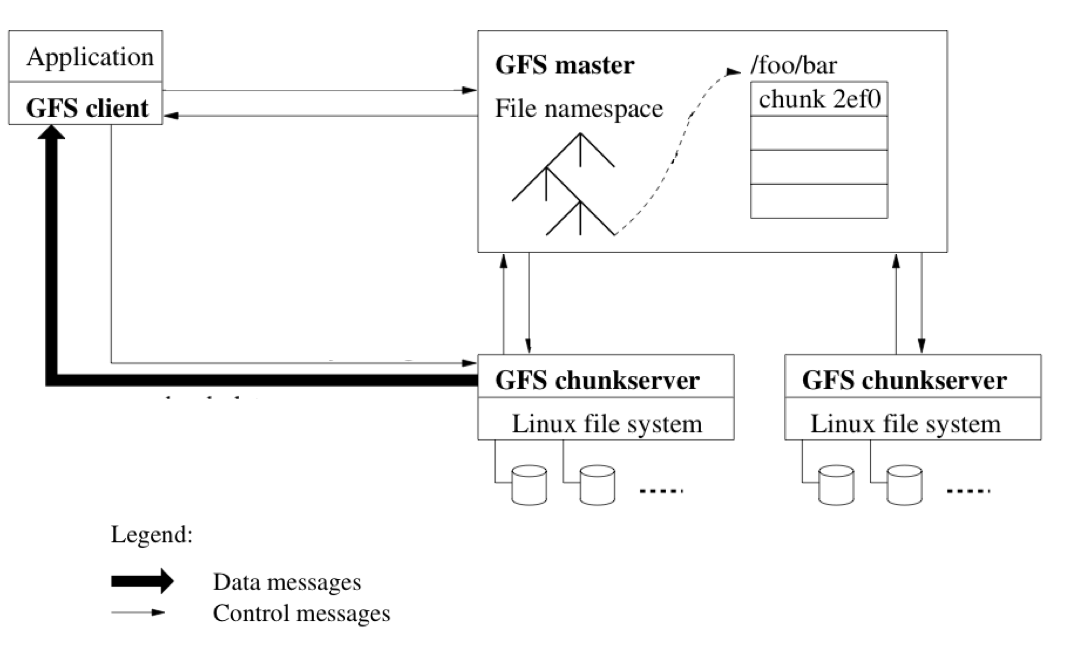
GFS的master server存储所有的metadata,负责与Client通信并且保证系统的一致性,同时通过与Chunk servers通信来迁移数据。Master server将所有的metadata存在RAM中,因此具有很快的速度。Chunk server对于data没有整体性的认知,通过与master sever通信来传递/更新数据。Chunk server不缓存任何数据,数据存在硬盘的block中,定期向master server发送heartbeat。Client缓存metadata,不缓存任何数据,通过与master server进行W/R操作访问数据。
GFS Client Read
- Client sends master: read(file name, chunk index)
- Master’s reply: chunk ID, chunk version number, locations of replicas
- Client sends “closest” chunkserver with replica:
- read (chunk ID, byte range)
- “Closest” determined by IP address on simple rack based network topology
- Chunkserver replies with data
GFS Client Write
- All replicas acknowledge data write to client
- Client sends write request to primary (commit phase)
- Primary assigns serial number to write request, providing ordering
- Primary forwards write request with same serial number to secondary replicas
- Secondary replicas all reply to primary after completing writes in the same order
- Primary replies to client
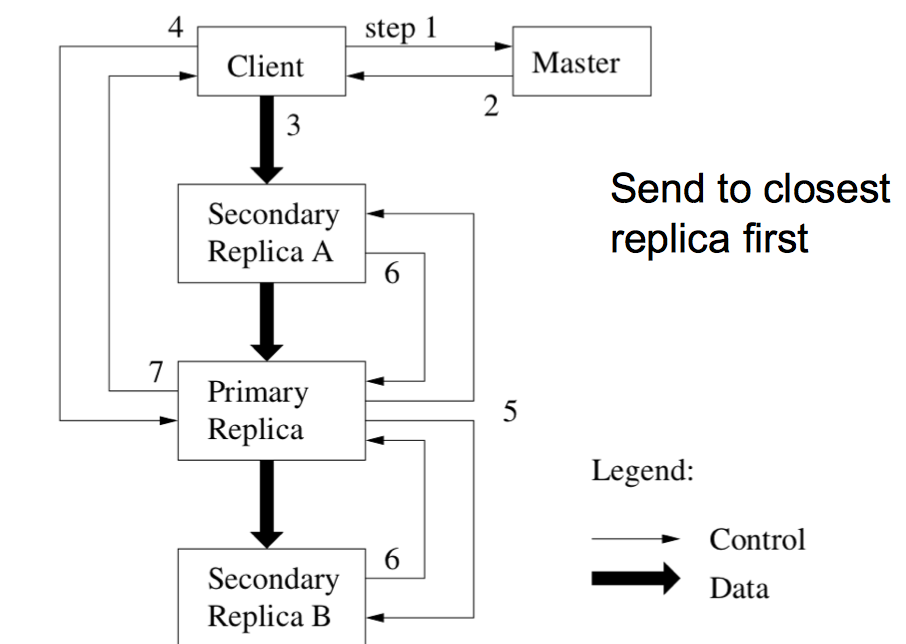
GFS的写操作,数据从Client流向最近的replica,直到所有的replica都得到了更新的数据。Replica得到了更新的数据后会与primary通信。Primary知道所有的replica都到了更新会通知Client。
GFS Consistency Model
- Changes to data are primary ordered as chosen by a primary
- Record append completes at least once, at offset of GFS’s choosing
- Failures can cause inconsistency
GFS Limitations
- Master biggest impediment to scaling
- Performance bottleneck
- Holds all data structures in memory
- Takes long time to rebuild metadata
- Must vulnerable point for reliability
- Solution:
- Have systems with multiple master nodes, all sharing set of chunk servers.
- Not a uniform name space.
- Large chunk size
- Can’t afford to make smaller, since this would create more work for master.
GFS Summary
- Success: used actively by Google to support search service and other applications
- Semantics not transparent to apps
- Must verify file contents to avoid inconsistent regions, repeated appends (at least once)
- Performance not good for all apps
- Assumes read once, write once workload (no client caching!)
HDFS
Hadoop file system, 和GFS非常相似。将master server换成name node,chunk server换做data note,chunk大小不是64MB而是128MB。结构几乎一致。没有什么重点的样子。
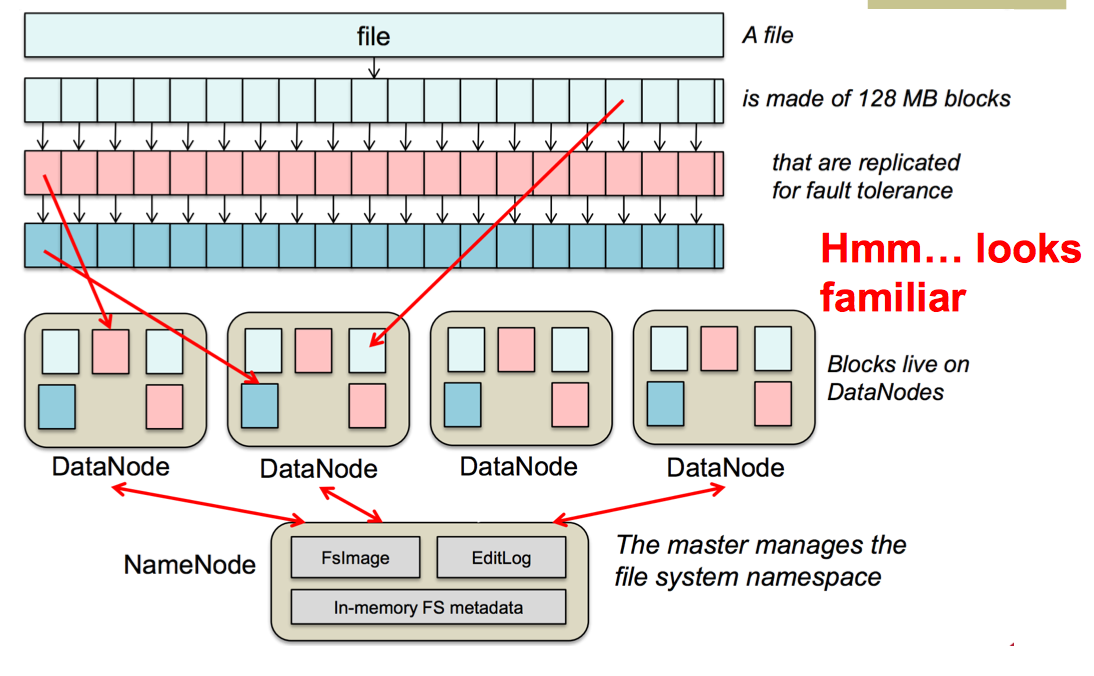
GFS Vs HDFS
### Spanner
…四天后 事实证明我的话假期果然很难进行学术活动_(:з」∠)_
Spanner,谷歌的分布式数据库,然而谷歌不给我面试,不想写Spanner,气愤。
数据库嘛,SQL语言,ACID什么的。对于分布式的事务具有外部一致性的特征,利用2PC实现。Fault-tolerance和replica基于Paxos实现。Spanner的中心思想是对于每个Transaction保存一个时间段(作为Timestamp),根据两个时间段是否重叠来判断两个事务的发生次序, Timetamp的顺序就是commit的顺序。我已经全忘了
Spanner Concurrency Control
Key aspect of differentiating Spanner – using globally meaningful timestamps for distributed transactions in achieving external consistency
对于每个Transaction,当天时间分别+-时间段ε(好像一般是传输时间来着),构成时间段。
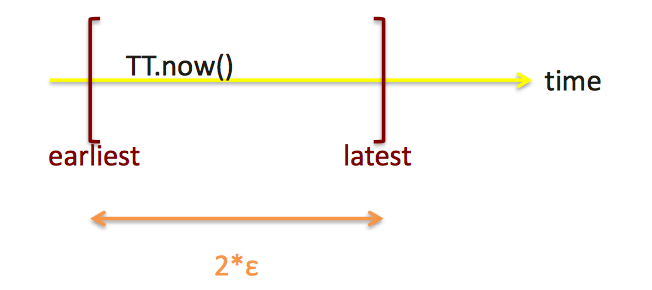
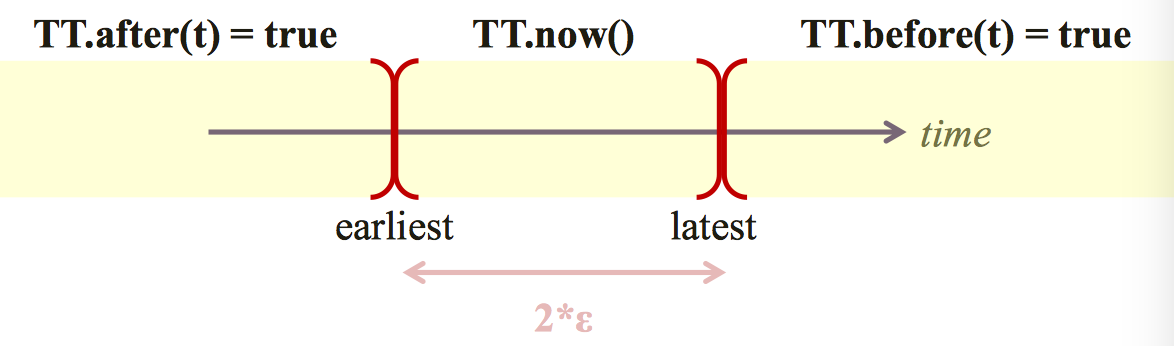
保证外部一致性也就是,如果T1事务的结束比T2事务的开始早,可以认为T1的timestamp小于T2.
参考资料: