Distributed System X
假装时差不存在并不代表时差真的不存在ORZ。这一篇关于Virualization, 介绍不同种类Virtualization异同,Container和Docker。
Virtualization: “a technique for hiding the physical characteristics of computing resources from the way in which other systems, applications, or end users interact with those resources. This includes making a single physical resource appear to function as multiple logical resources; or it can include making multiple physical resources appear as a single logical resource”
Motivation: virtual machine, isolation
| Physical Machine | Virtual Machine |
|---|---|
| physical hardware + software | sofeware abstraction + virtualization layer |
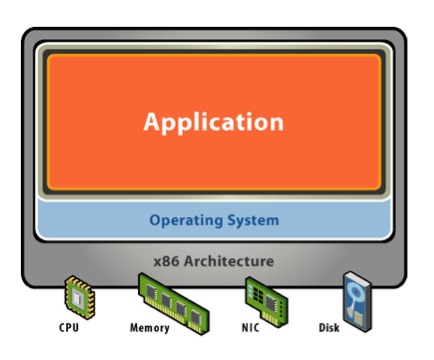 |
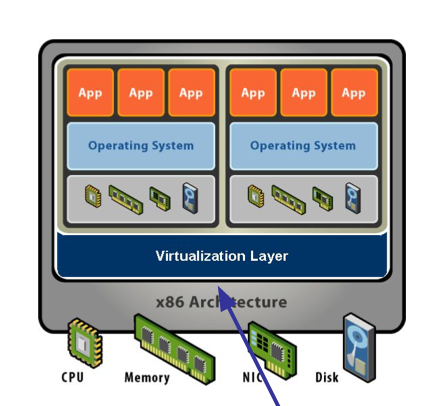 |
| Properties: | fidelity, perfomance, safety and isolation |
Types of Virtualization
System virtualiation: Virtualizing the entire hardware and software layers
- Type1 Naive/Bare metal
- Higher performance
- VMWare ESX, Xen, Hyper-V
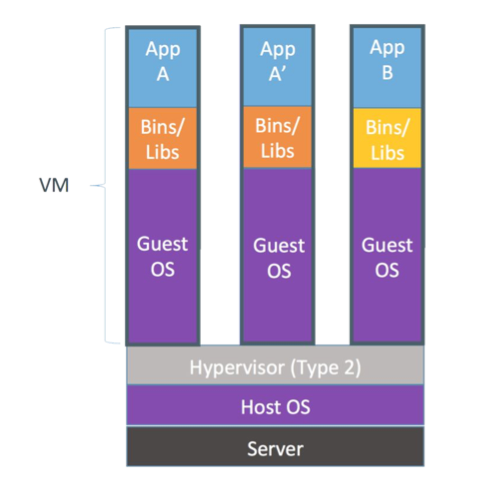
- Type2 Hosted
- Easier to install
- Leverage host’s device drivers
- VMware Workstation, Parallels
Process virtualization: Virtualizing OS resources between processes
- Language-level: Java, .NET, Smalltalk
- OS-level : Solaris Zones, BSD Jails, Linux namespace
Full virtualization
- Unmodified OS, virtualization is transparent to OS
- VM looks exactly like a physical machine
Para virtualization
- OS modified to be virtualized
- Better performance at cost of transparency
Requirment of Virtualization
- Isolation: fault/performance
- Encapsulation: capture all VM states/enables VM snapshots or clones
- Portability: independent of physical hardware/enables migration/easy clone
- Interposition: transformations on instructions, memory, I/O
Implement
Processor Virtualization
All instructions either privileged or non-privileged
- Privileged instruction: trap
- Non-privileged instruction: execute natively
- CPU virtualization: trap-and-emulate
- Special instructions: behaves differently depending on the CPU state
- Solution: replace non-virtualizable instructions with easily Virtualized ones statically(Para)/perform binary translation(Full)/supports “guest” model
Memory Virtualization
- OS assumes that it has full control over memory
- VMM partitions memory among VMs
- Abstrations: logical/physical/machine
Memory Management
- VMMs tend to have simple memory management
- More sophistication: Overcommit with ballooning
- Even more sophistication: memory de-duplication
I/O Virtualization
- Direct access: VMs can directly access to devices
- Shared access: VMM provides an emulated device and routes I/O data to and from the device and VMs
- Overall I/O is complicated for VMMs
- Networking also complex as VMM and guests all need network access
Storage Management
- VMM provides both boot disk + other storage
- Type 1 - storage guest root disks and config
- Type 2 - store as files in the host file system/OS
- VMM also usually provides access to network attached storage (just networking) => live migration
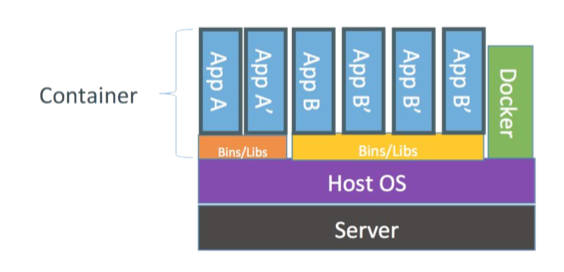
Container
Motivation:
- I/O, memory, disk overhead of virtual machines
- Startup latency of virtual machines
Ideas:
- Multiple isolated instances of programs
- Running in user-space (shared kernel)
- Instances see only resources (files, devices) assigned to their container
Requirements:
- Isolation and encapsulation
- Low overhead
- Operation System support
Key problems:
- Isolating which resources containers see
- each process is assigned a “namespace”
- Isolating resource usage (security & performance)
- usage counters for groups of processes (cgroups)
- Efficient per-container filesystems
- layering of filesystems (copy on write)
Advantages:
- Fast boot times
- High density
- Very small I/O overhead
Limitations:
- No isolation guarantee for some resources
- Resources that are not managed by the kernel
- Large attack surface under adversarial behavior
- Containers typically have access to all syscalls
- One approach: syscall filtering
| VMs | Containers |
|---|---|
| strong isolation guarantees and security | fast startup times, negligible I/O overheads, very high density |
| OS startup, disk,memory, and hypervisor overhead | weak security isolation |
| isolate between different users | isolate different applications/services of a single user |
参考资料: