Deep Learning I
当然首先是关于神经网络的基础知识和训练算法。
深度学习很火,学学看看。也不是说什么火就要学什么。瞎学西西╮(╯▽╰)╭
可我还是想学数据库。执念。这学期的高级数据库不适合我。哭唧唧。
但是为了加深印象还是要写笔记。
首先介绍了背景知识,Connectionist Machines, A-type, B-type machines, brain models, Hebbian learning, Rosenblatt’s perceptron什么的。觉得这些了解一下就好,perceptron学过好几次,是很重要的概念。
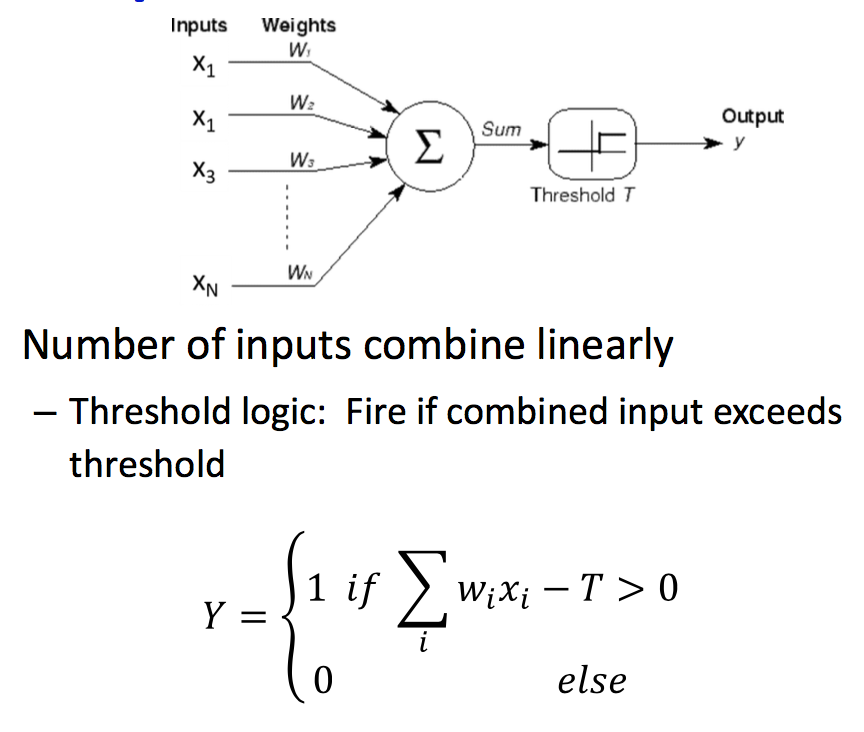
Perceptron 感知机
机器学习的经典模型感知机,一种二元分类器,将输入向量x映射到二元输出值y上。
Sequential learning:
- Update the weights whenever the perceptron output is wrong
- Proved convergence
二元感知机可以看线性分类器,可以表示所有除了XOR外的boolean操作。
Activation 激活函数: The function that acts on the weighted combination of inputs (and threshold)
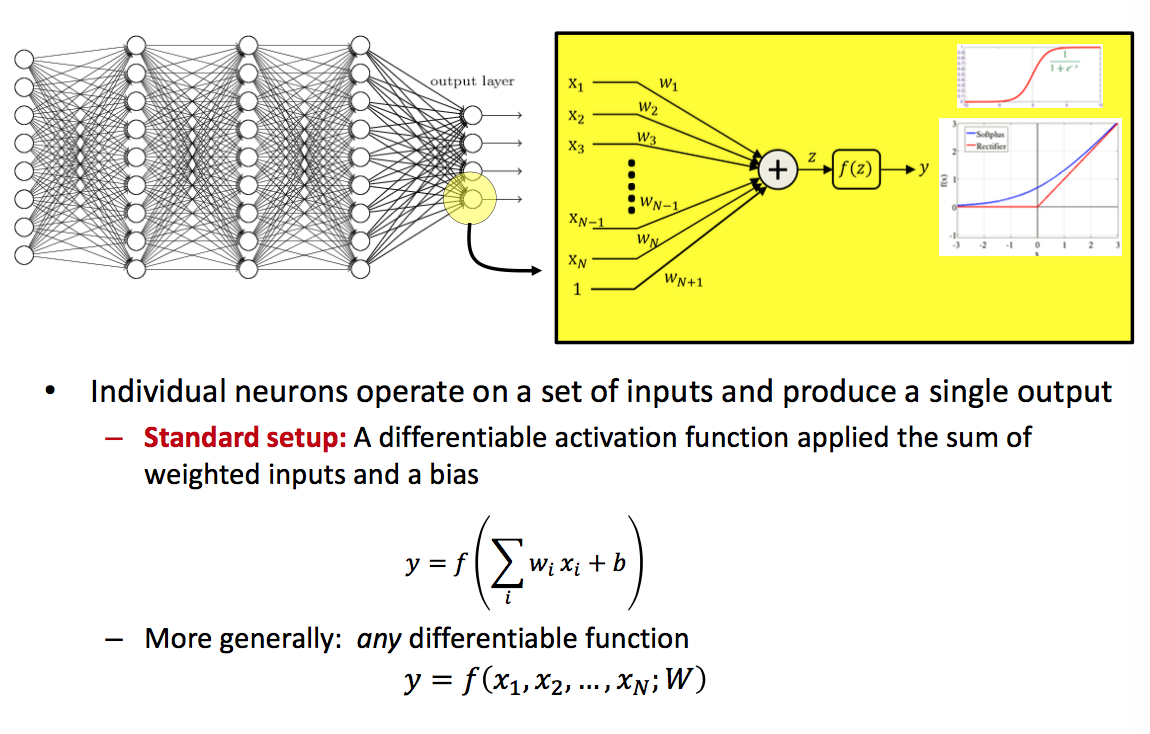
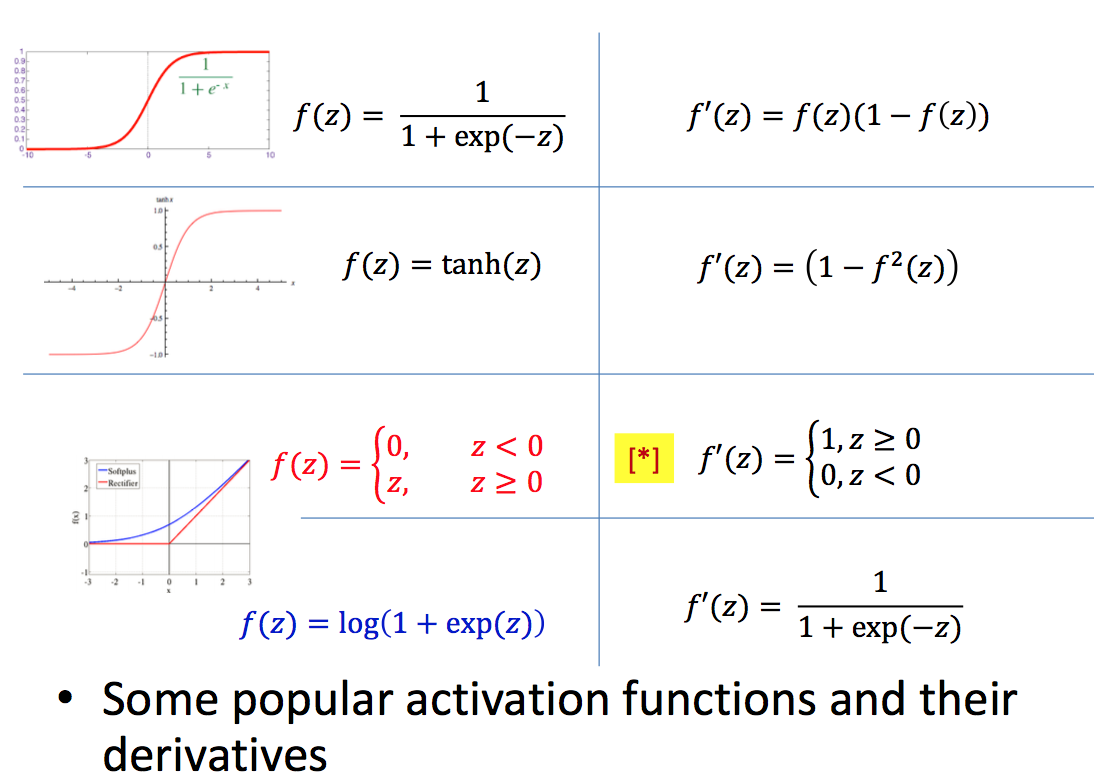
一般是sigmod?第一次作业实现了sigmod,tanh,relu。作为激活函数,要求是可导并且非线性。
MLP
多层感知机,可以将输入向量映射到输出向量。克服了单个感知机无法识别线性不可分数据的弱点。
- MLPs are connectionist computational models
- Individual perceptrons are computational equivalent of neurons
- MLP is a layered composition of many perceptrons
- MLPs can model any Boolean functions
- Individual perceptrons can act as Boolean gates
- Networks of perceptrons are Boolean functions
- MLPs are Boolean machines
- They can represent arbitrary decision boundaries
- They can be used to classify data
- MLP can also model continuous valued functions
- MLPs are classification engines
- MLP can also model continuous valued functions
Background介绍完后就进入deep学习,depth > 2 算作deep。
由于boolean function可以看作真值表的集合,所以用单隐层的MLP就可以表示所有的boolean function。
对于single-layer boolean network:
- 2^N-1 perceptrons in hidden layer - exponential
- O(N2^N-1) weights - superexponential
同样的boolean function,以所有输入的XOR为例子:
- 3N-1 perceptrons in deep network
- 9(N-1) parameters - linear
- can be arranged in 2log2(N) layers
得出结论:
- Reducing the number of layers below the minimum will result in anexponentially sized network to express the function fully
- A network with fewer than the minimum required number of neurons cannot model the function
- Any Boolean circuit of depth d using AND, OR and NOT gates with unbounded fan-in must have size 2^(n^1/d)
Shannon’s theorem: For n > 2, there is Boolean function of variables that requires at least 2^n/n gates

- For general case of mutually intersecting hyperplanes in D dimensions, we will need O(N^D/(D-1)!) weights (assuming N » D)
- Increasing input dimensions can increase the worst-case size of the shallower network exponentially, but not the XOR net
MLP也可以对连续值进行回归:
- An MLP with many units can model an arbitrary function over an input
- A one-layer MLP can model an arbitrary function of a single input
- MLPs with additive output units are universal approximators
- A neural network can represent any function provided it has sufficient capacity
- Not all architectures can represent any function
一个课件一百多页ppt为什么我写笔记却只有几行(._.)
Neural Network
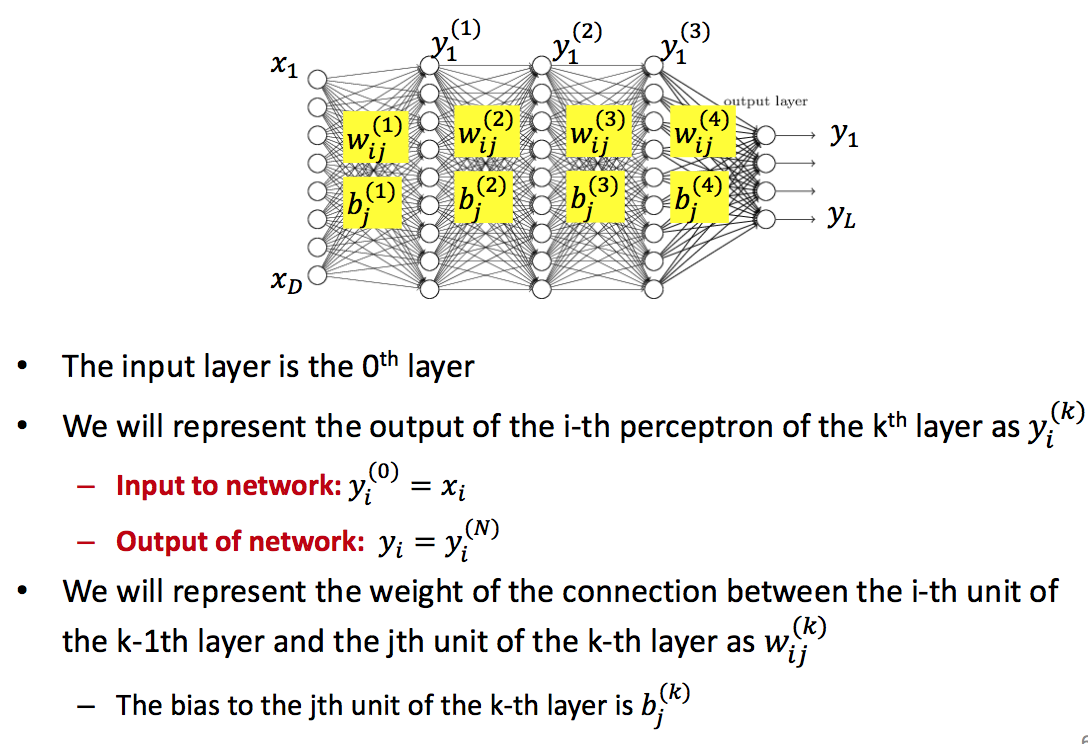
Architecture: MLPs
Parameters: weights and bias
Learning: determine value of parameters so network computes desired function
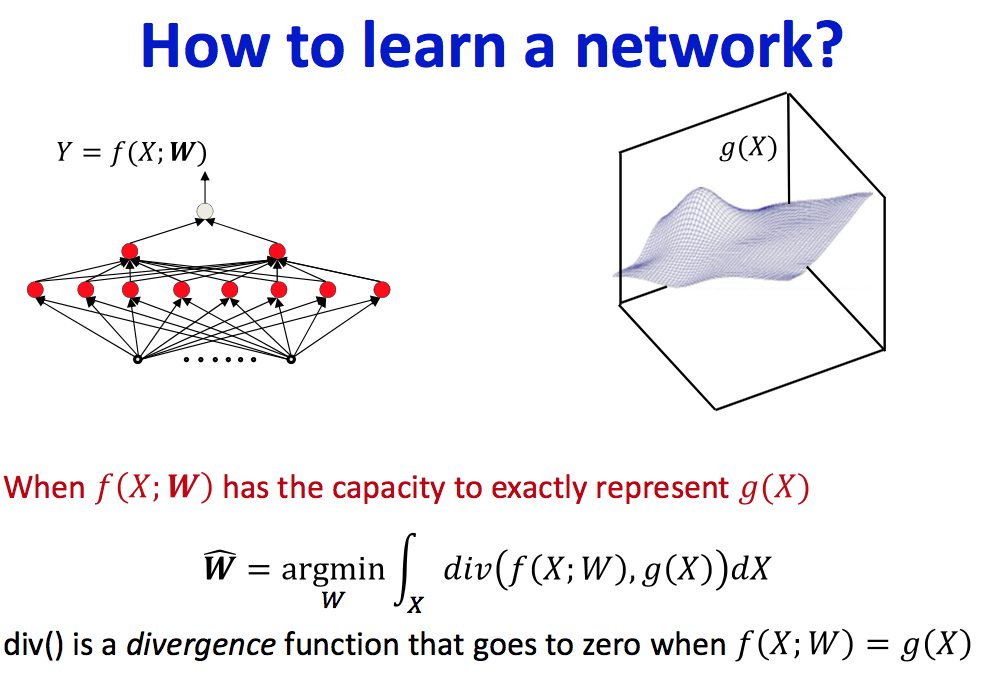
- More generally, given the function to model, we can derive the parameters of the network to model it, through computation
不过一般情况下g(X)是不知道的:Sampling g(x)
- Basically,get input-output pairs for a number of samples of input , many samples (𝑋 , 𝑑 ), where 𝑑 = 𝑔(𝑋) + 𝑛𝑜𝑖𝑠𝑒
- Good sampling: the samples of X will be drawn from P(X)
Learning function: estimate the network parameters to “fit” the training points exactly
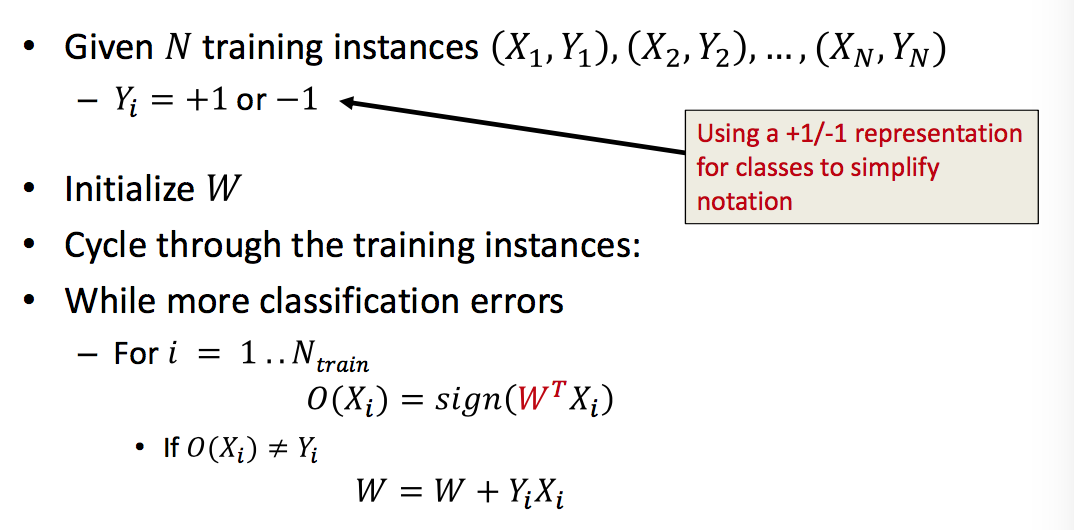
Perceptron Learning Algorithm
| Perceptron learning algo | Summary |
|---|---|
 |
 |
- Guaranteed to converge if classes are linearly separable
- After no more than (R/r)^2 misclassifications
Greddy algorithms
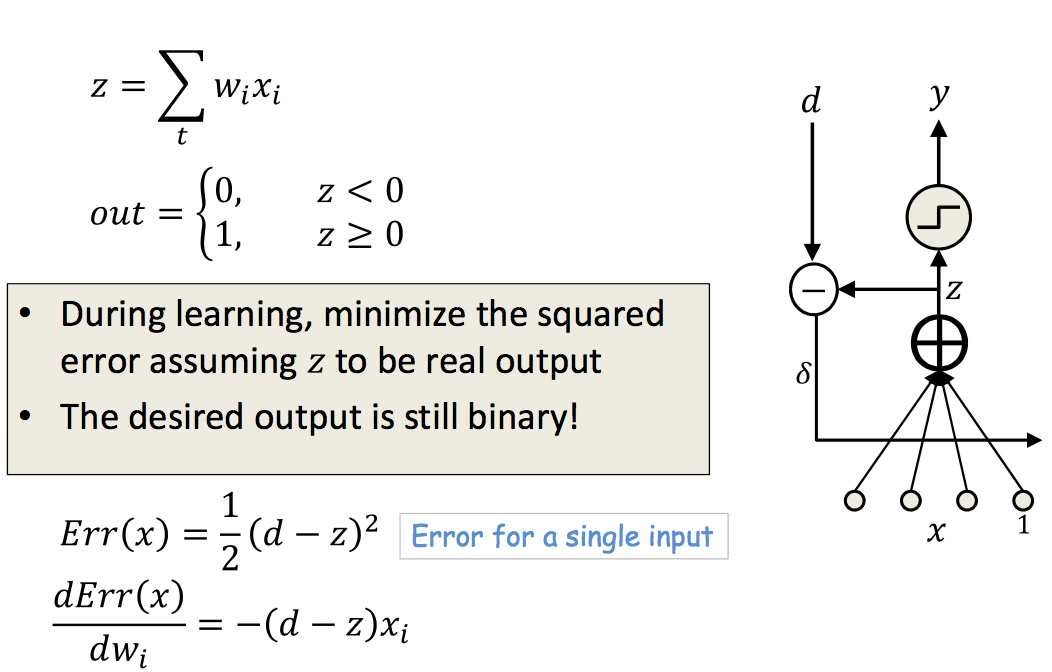
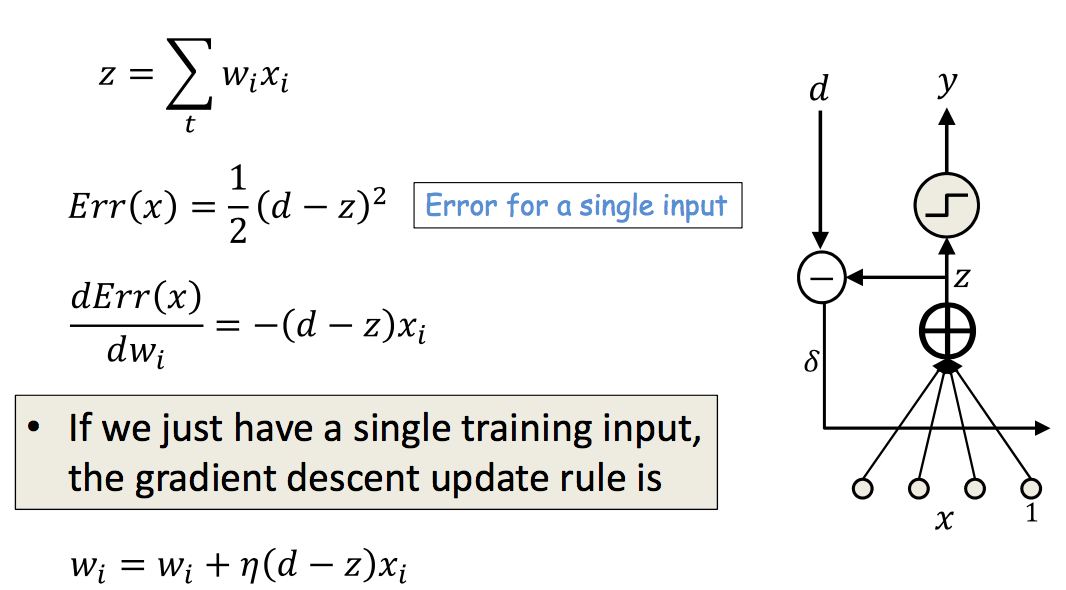
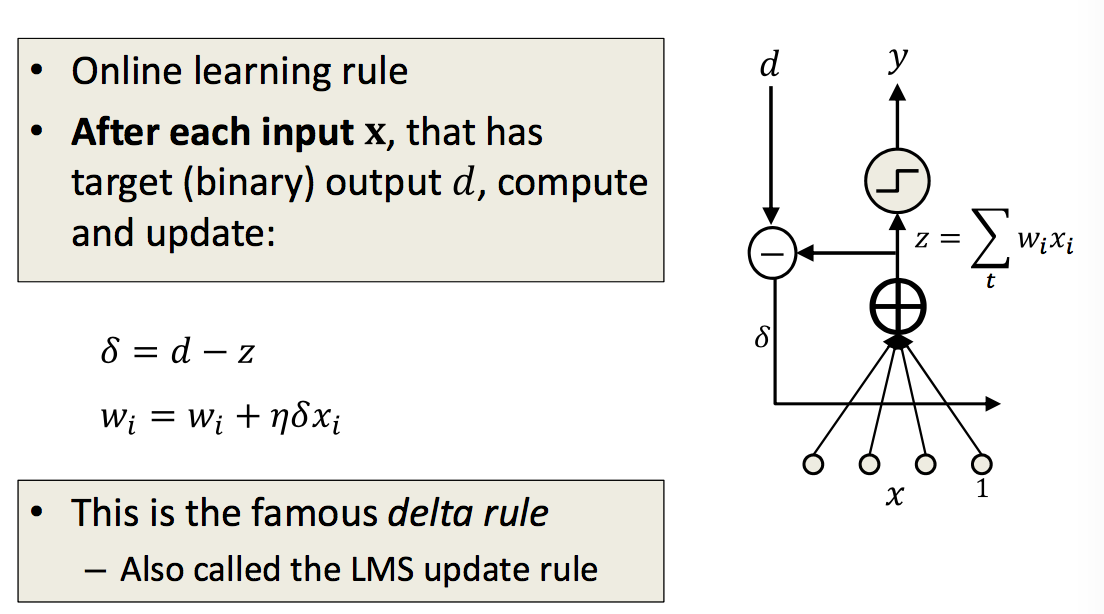
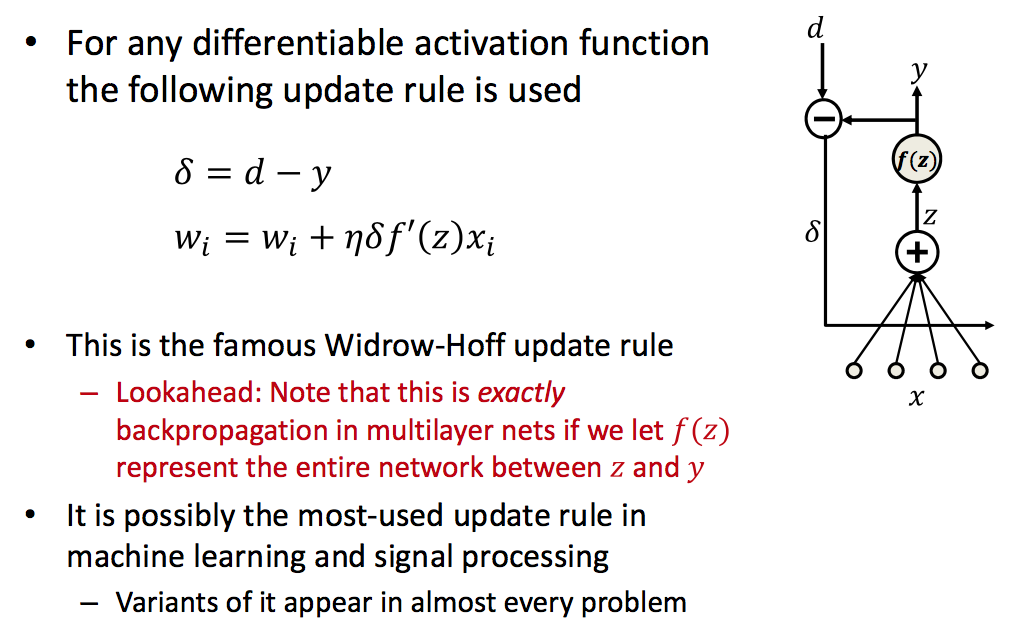
ADALINE: Adaptive Linear Neuron
| Learning | Rule |
|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
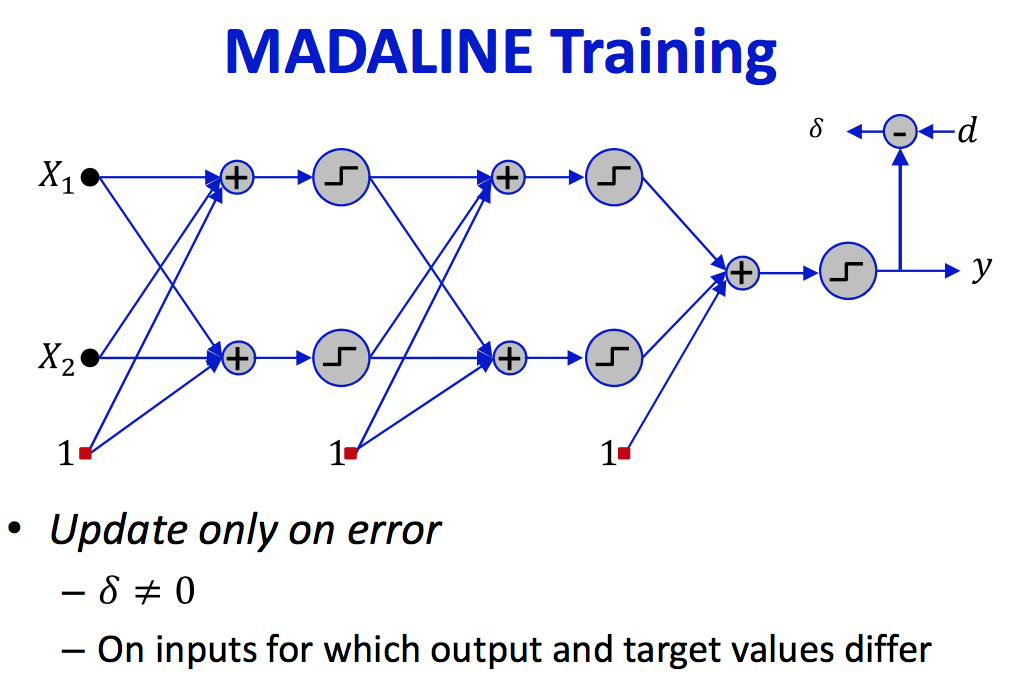
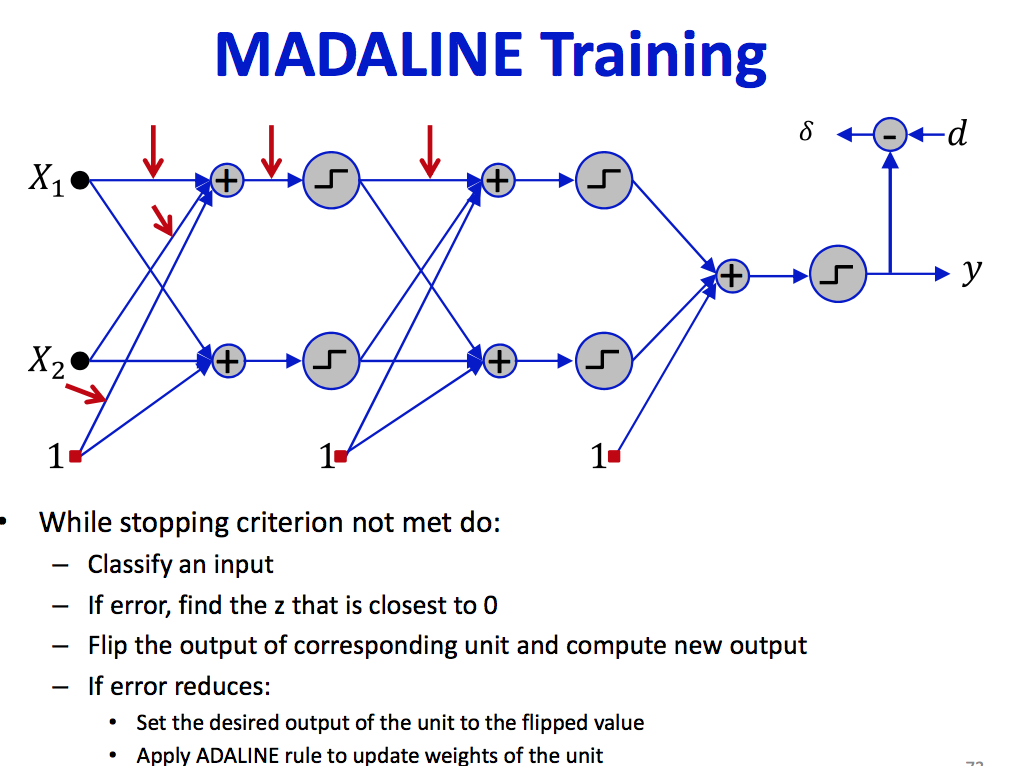
MADLINE: Multiple adaline
- Not very useful for large nets, effective for small networks - too expensive/greedy
| Training | Learning |
|---|---|
 |
 |
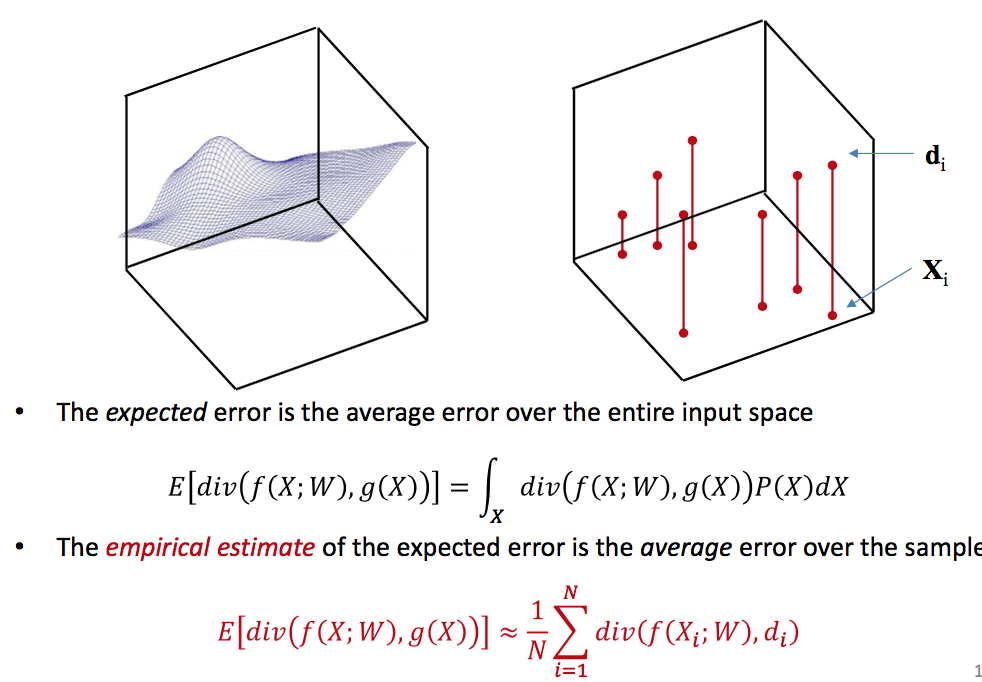
Risk & Error
Empirical risk
- The empirical risk is only an empirical approximation to the true risk which is our actual minimization objective
| Risk | Minimization |
|---|---|
 |
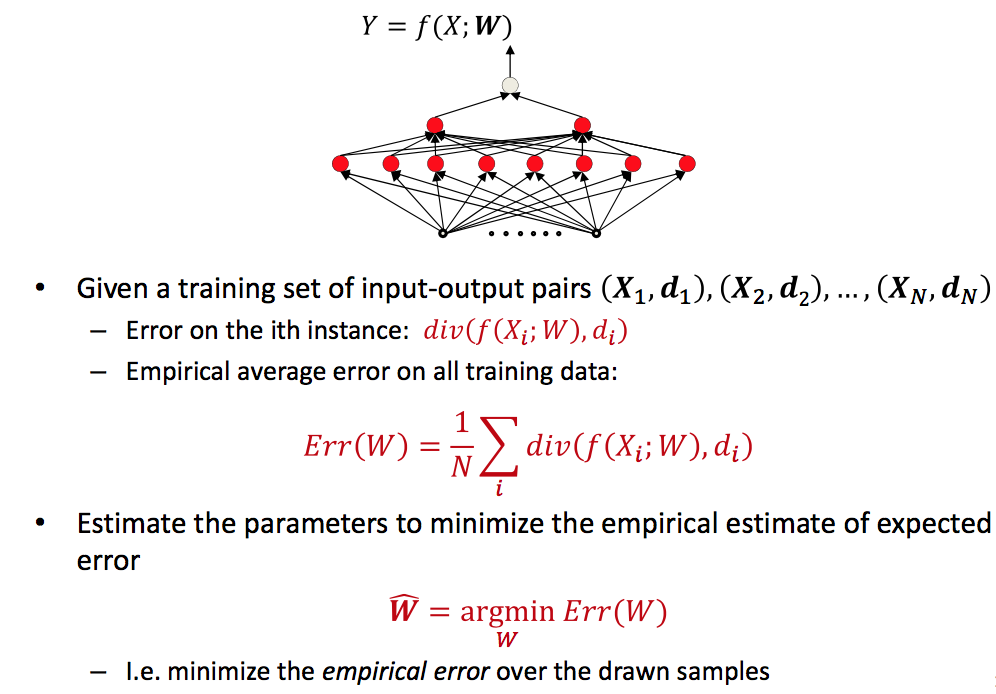 |
求使Err最小的W值,矩阵求导知识,由于失忆第一个作业疯狂推导好久。
Problem statement:
| Find min | Hession |
|---|---|
 |
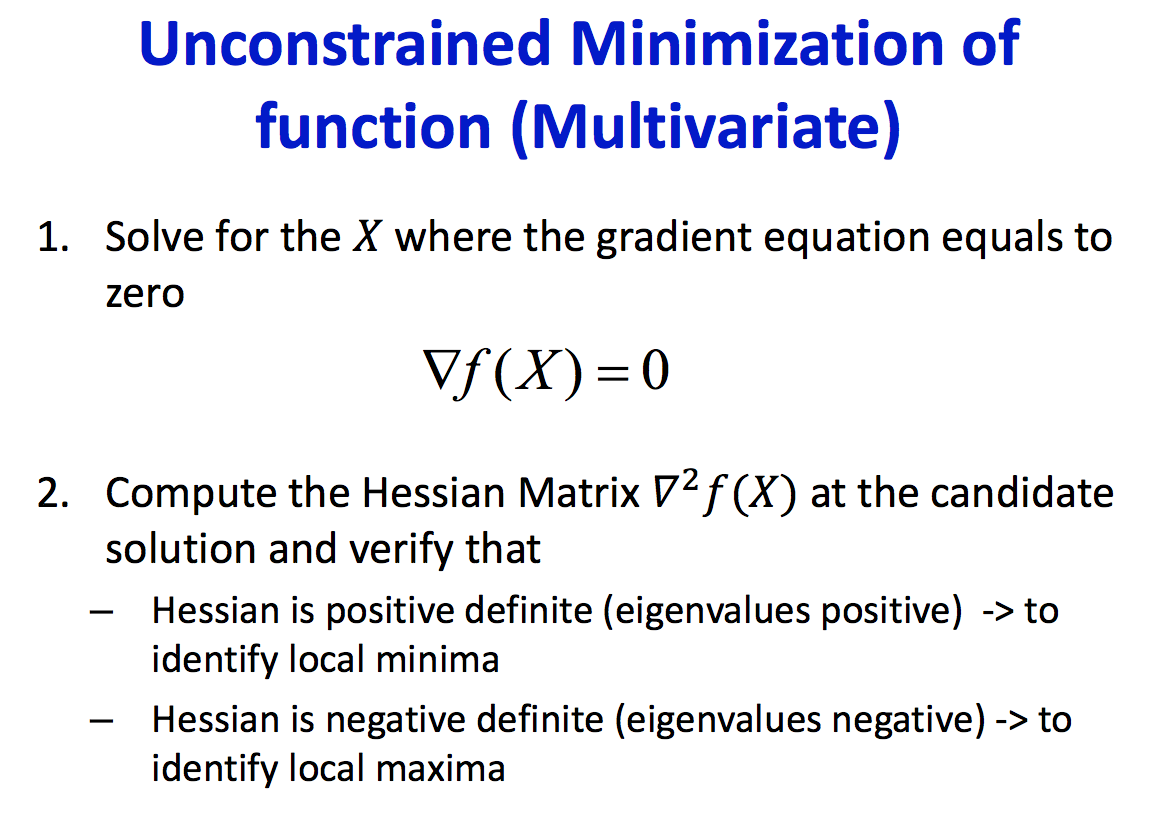 |
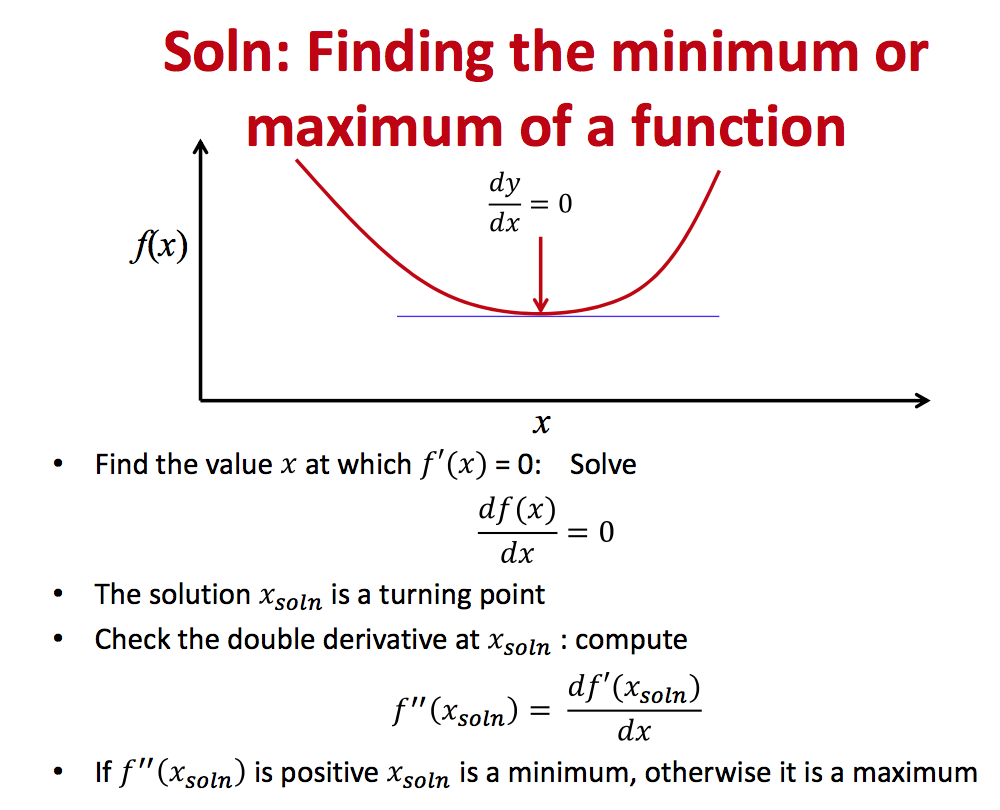
Solutions
| Closed Form | Iterative |
|---|---|
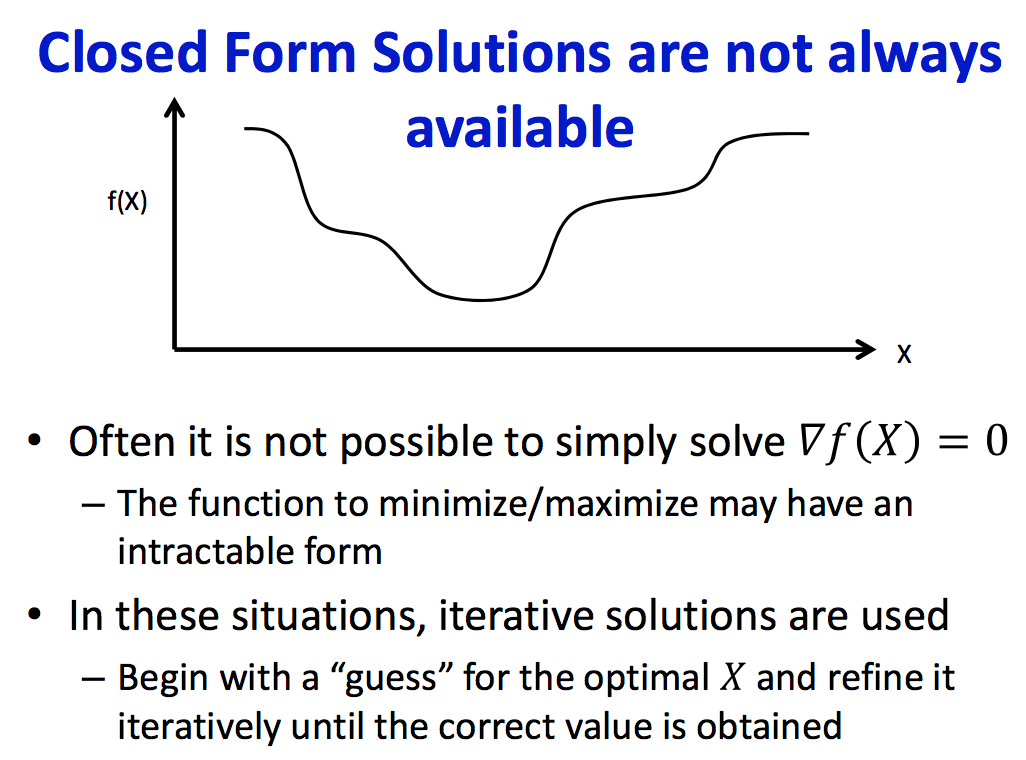 |
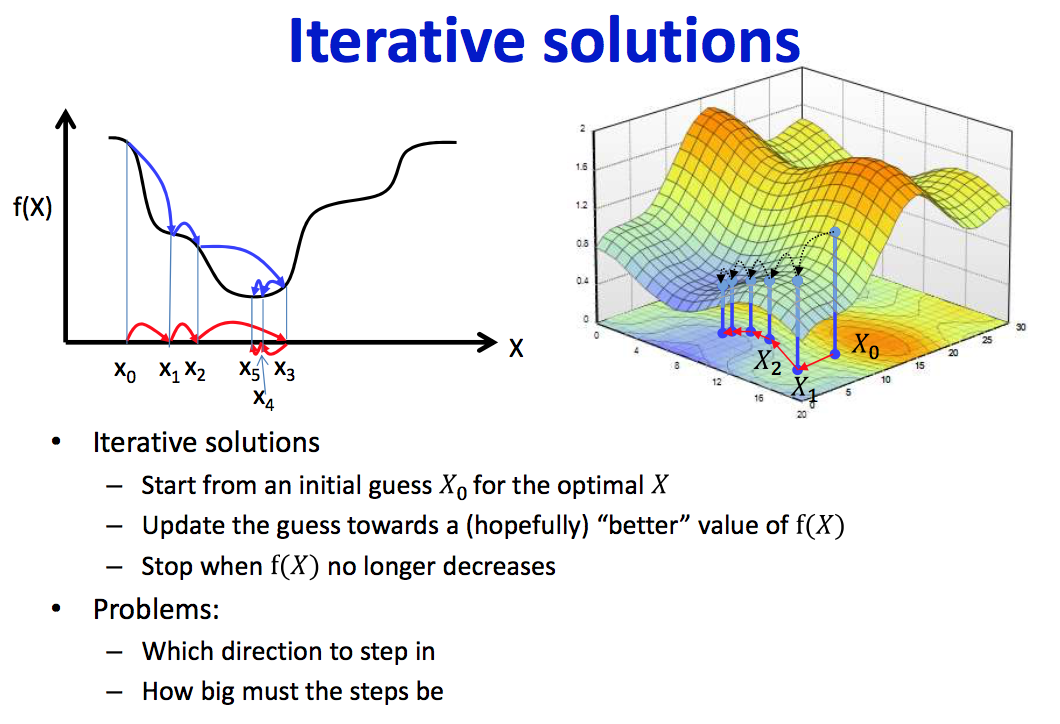 |
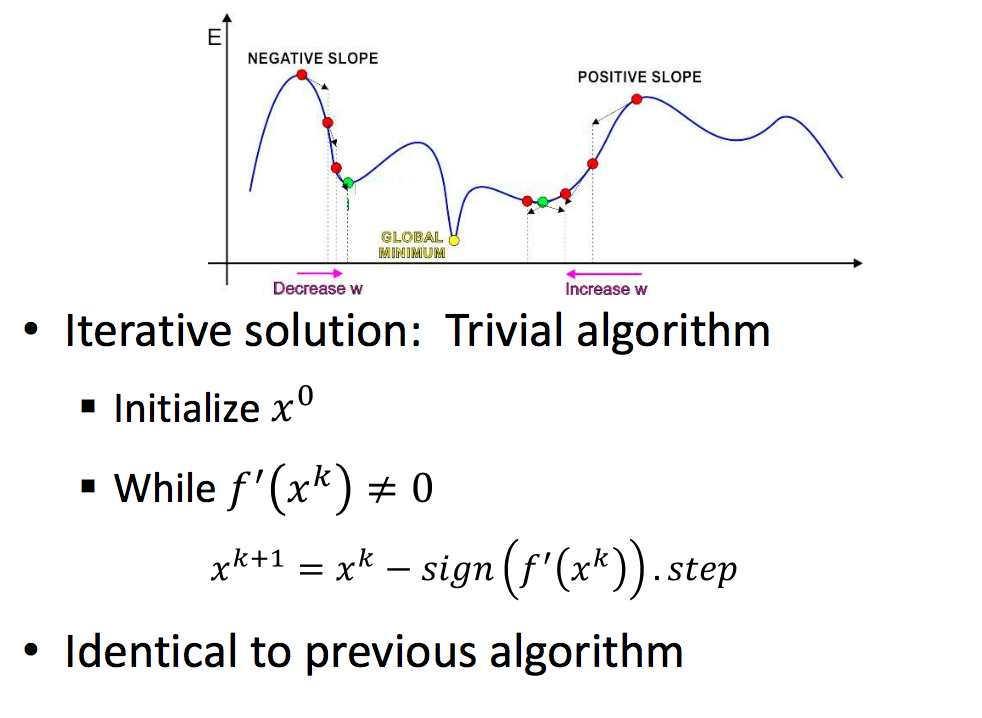
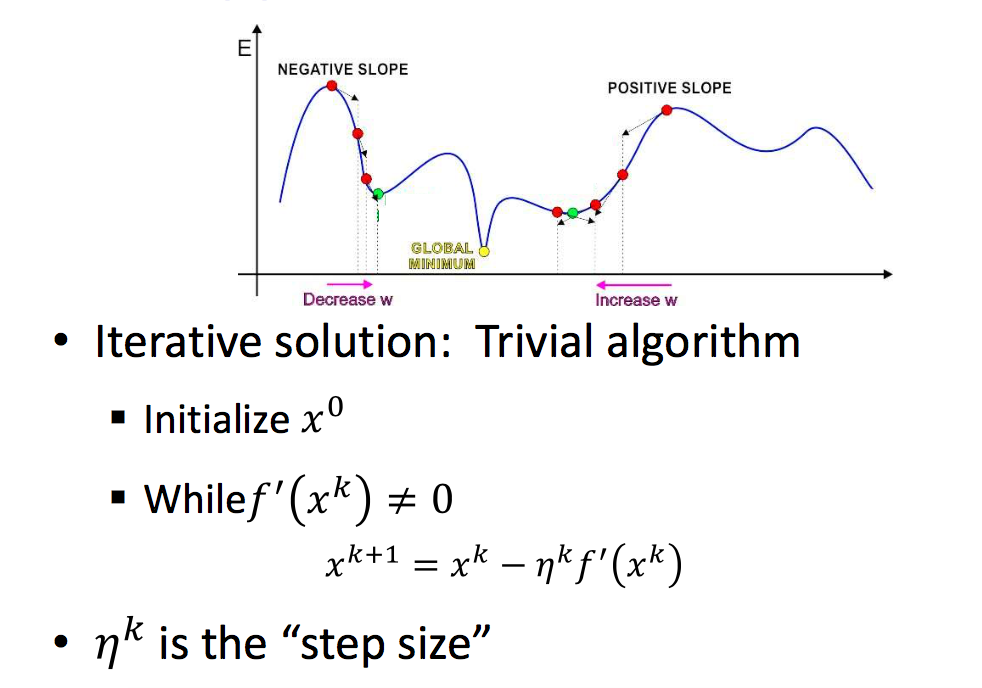
因为Closed form不一定可解,引入了迭代求解的方法,借此介绍非常常用的training算法梯度下降。
Gradient Descent
| Approach | Multivariate |
|---|---|
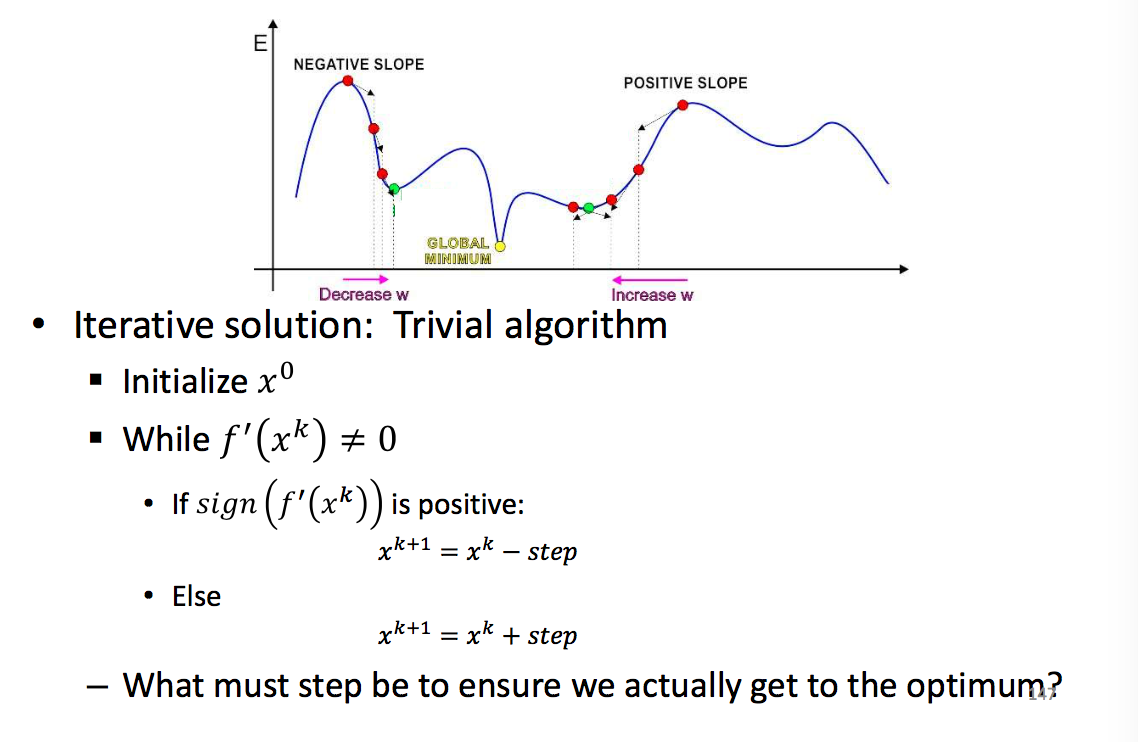 |
 |
 |
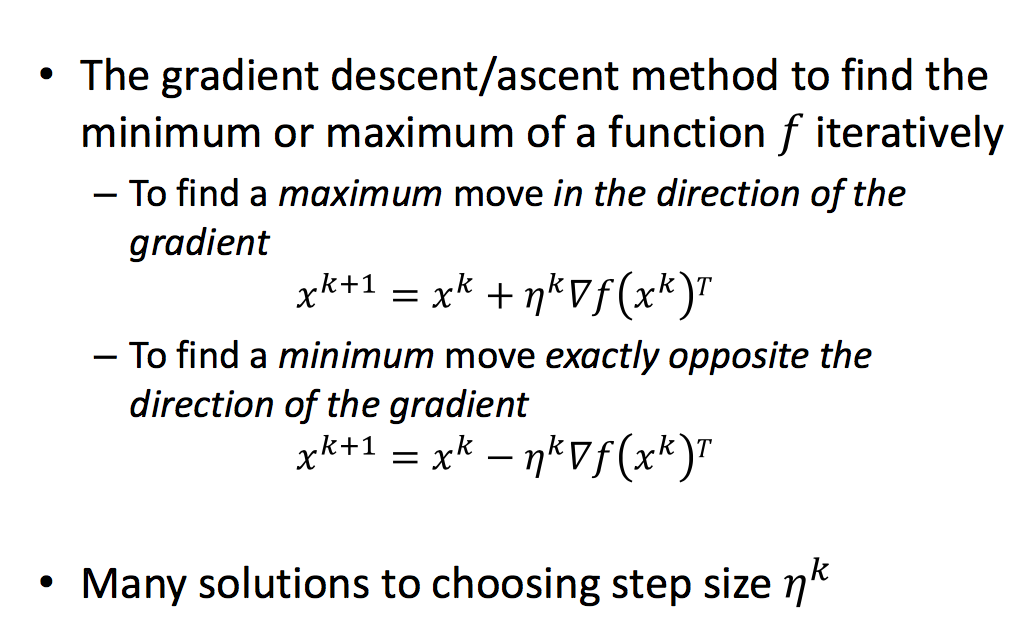 |
所以现在的问题变成如何通过GD来求解最优的参数使Objective(Err/Cost)达到最小。
Problem statemet:
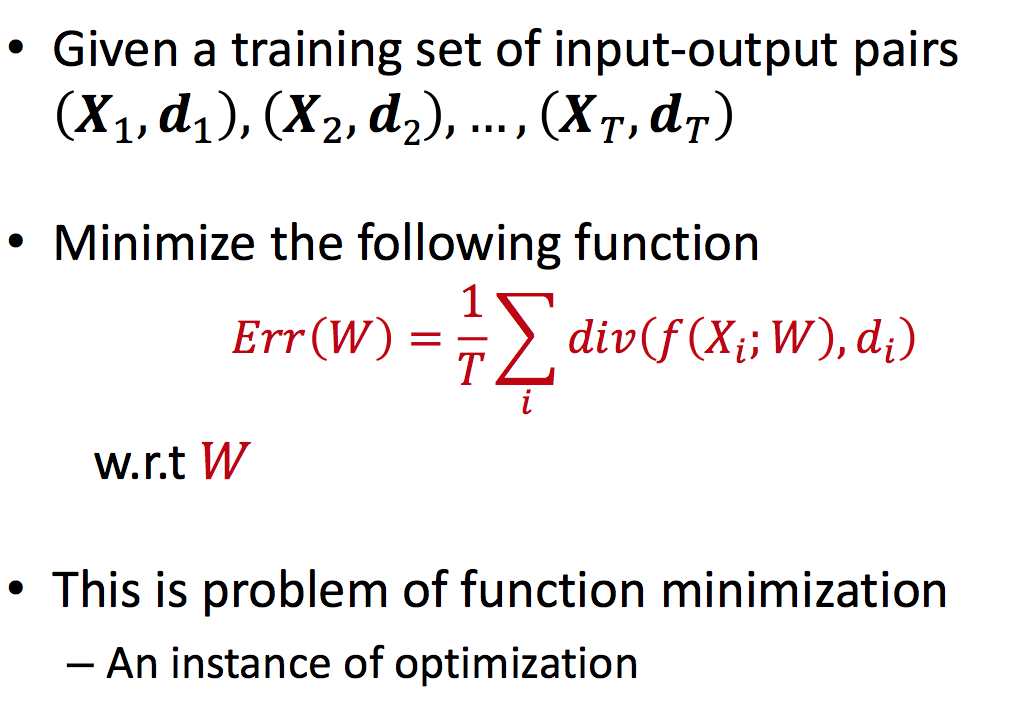
其中(X, d)是input, 用矩阵形式表示, W是神经网络的parameters,也就是我们要得到的训练结果, div计算通过神经网络predict的值与真值的err, 也就是objective目标方程,𝑓表示这个网络。
Network Construction
| Individual Neuron | Activations |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| Combination | Notation |
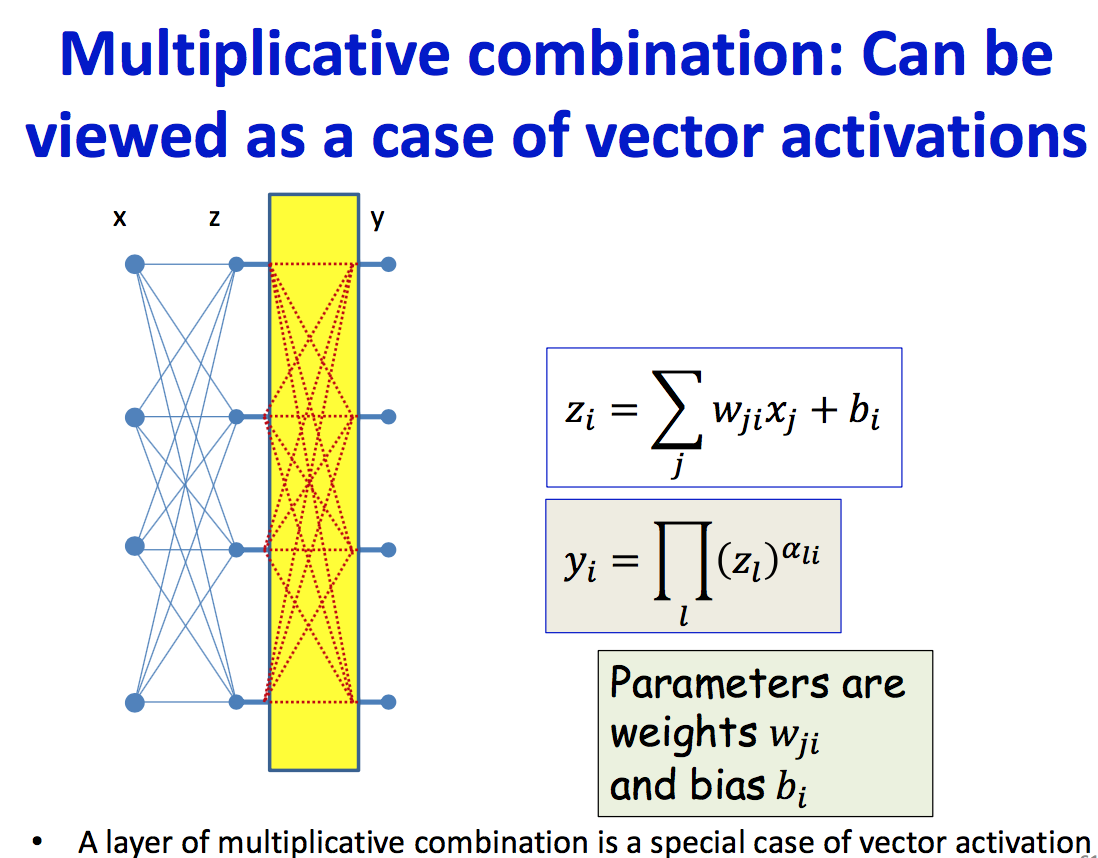 |
 |
Training by GD

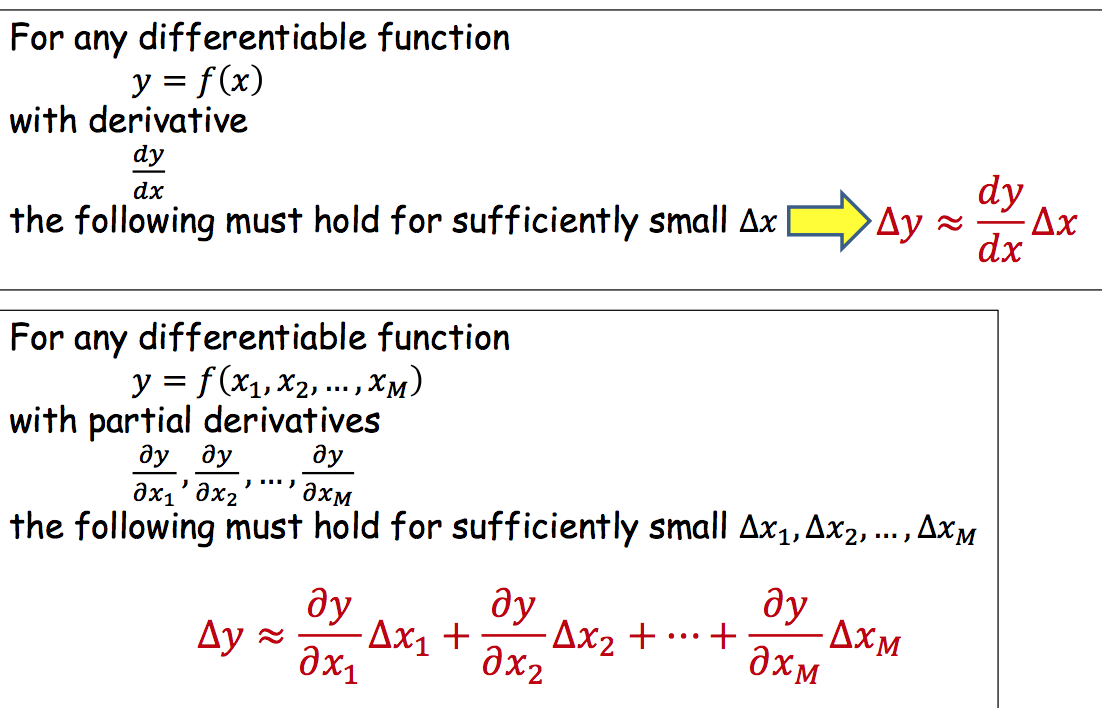
Objective对W的导数,是Objective对Wij导数的矩阵表达形式。利用chain rule从最后一层一层一层向前求导,直到得到结果。
| Chain rule | Network |
|---|---|
 |
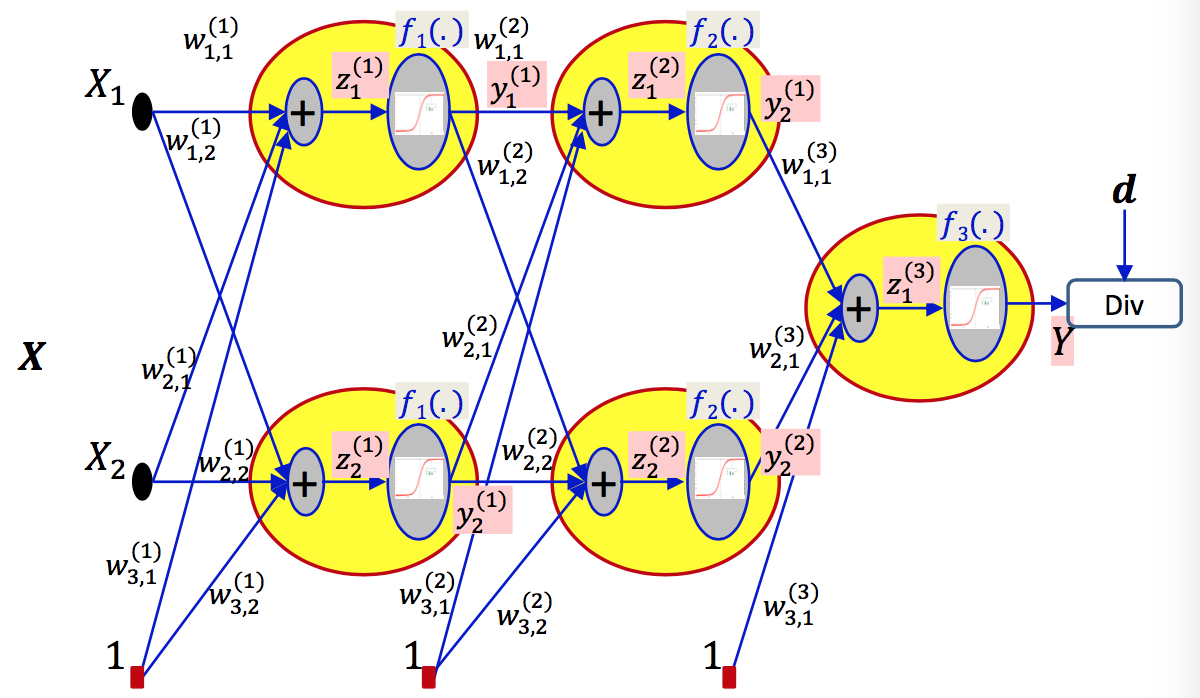 |
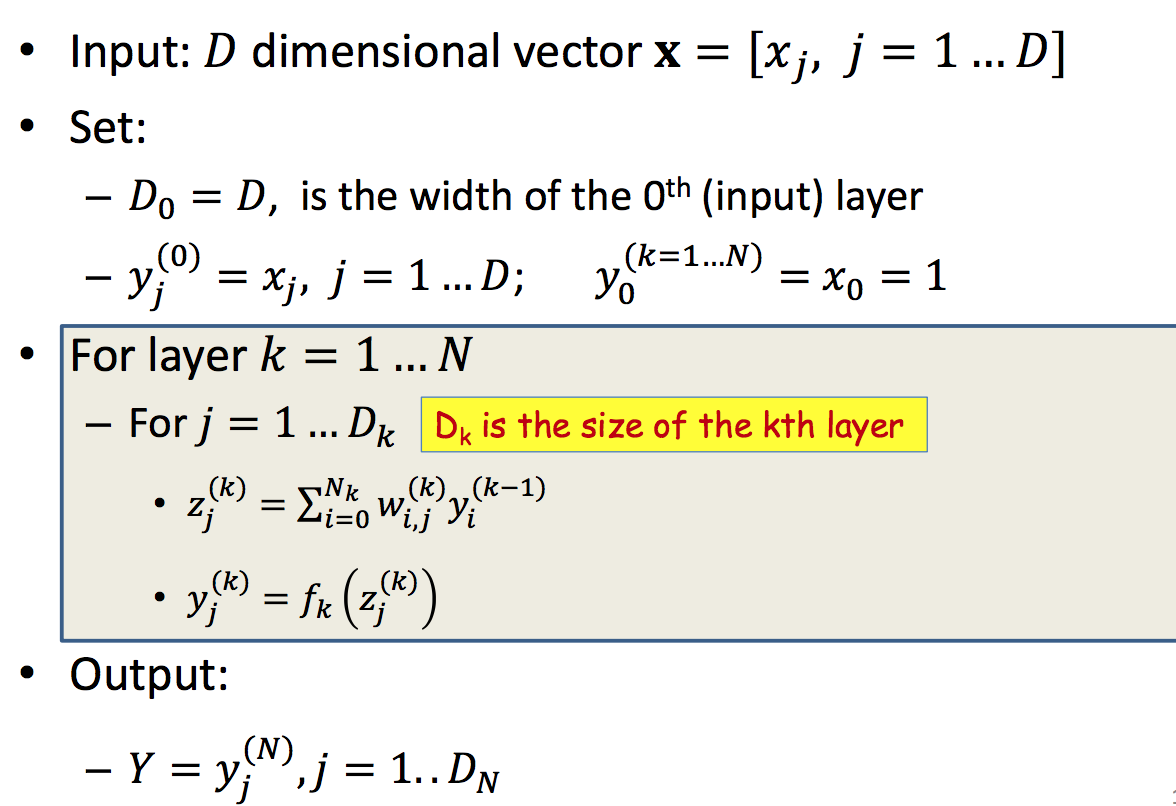
用梯度下降来训练神经网络,首先根据初始化的weights和bias计算出predict的值,根据objective function和ground truth得到loss/err. 为了得到使这个objective最小的weights和bias利用梯度下降来求解。因此需要backward computation,对每一层的weights和bias求出objective对它们的偏导,根据更新规则更新weights。不断重复这个过程直到收敛。
| Forward pass | Backward pass |
|---|---|
 |
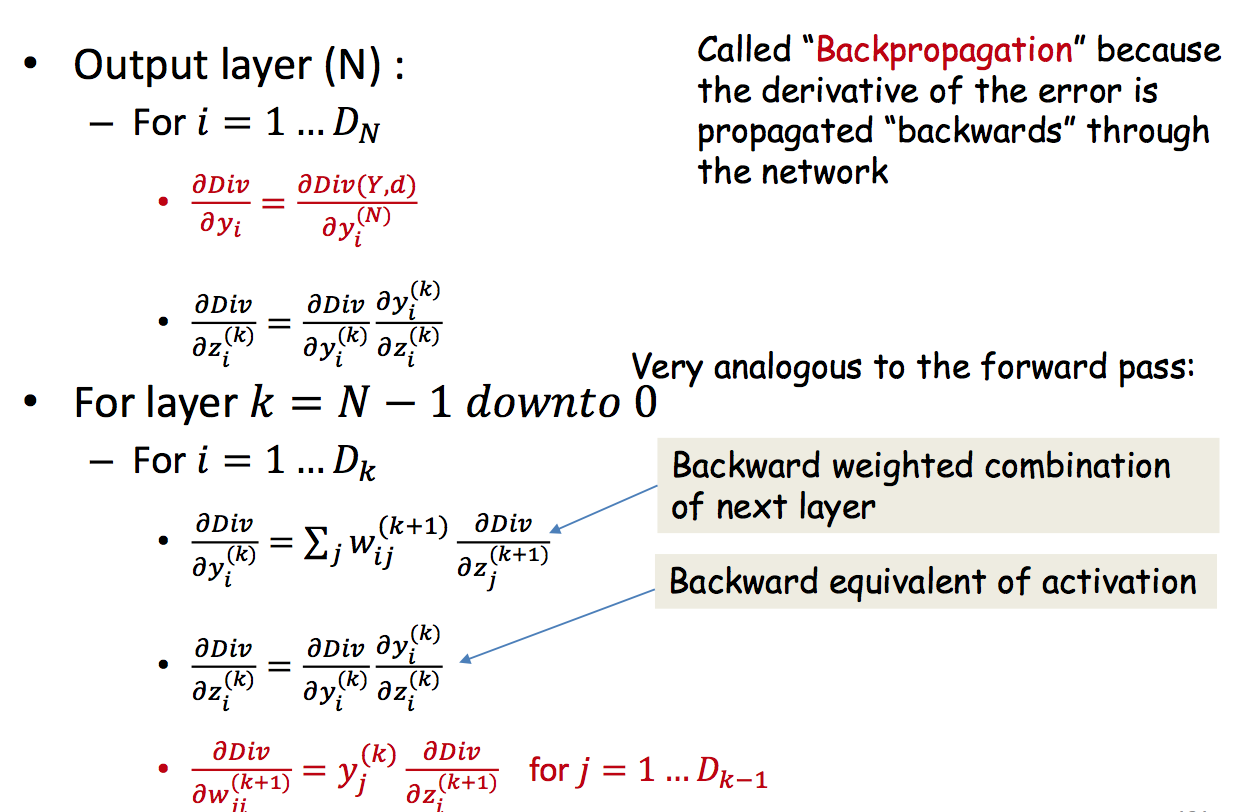 |
Training by BackProp
| Sudo code | Vector formulation |
|---|---|
 |
 |
- Assumptions: all these conditions are frequently not applicable
- The computation of the output of one neuron does not directly affect computation of other neurons in the same (or previous) layers
- Outputs of neurons only combine through weighted addition
- Activations are actually differentiable
- Vector activations: all outputs are functions of all inputs
前两周的内容基本都被之前的601和605覆盖了,不过时间久了也有些失忆,就当作复习一下。
参考资料
Multilayer Feedforward NEtworks
A Capacity Scaling Law for ANN
Learning representations by BP err