Parallel Architecture & Programing 壹
直到毕业我才写总结笔记,为我自己的颓废表示羞耻_(:з」∠)_ 学这一部分的时候我还分不清GPU和CPU…… 首先就先介绍了相关基础概念和硬件&软件方面的相关实现。
Forms of parallelism
Parallel Execution 并行执行
(想想我居然连编译器是做什么的都不知道:) 有机会上一下Compiler就好啦ಥ_ಥ
以Taylor展开的example program举例:
void sinx(int N, int terms, float* x, float* result)
{
for (int i=0; i<N; i++)
{
float value = x[i];
float numer = x[i] * x[i] * x[i]; intdenom=6; //3!
int sign = -1;
for (int j=1; j<=terms; j++)
{
value += sign * numer / denom;
numer *= x[i] * x[i];
denom *= (2*j+2) * (2*j+3);
sign *= -1;
}
result[i] += value;
}
}
Compiler: input: programs, output: sequence of instructions
Processors: run sequence of instructions, which means loading instruction from memory, figuring out what it means(decode), and having component act.
Simple Processor 单核处理器的基本结构:
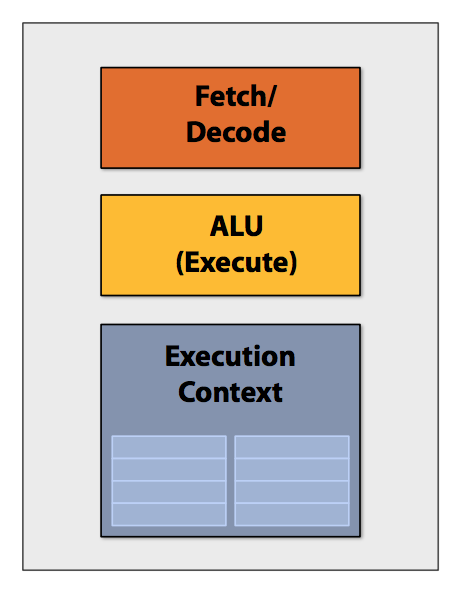
ALU*1, 1Execution Context*1, execute one instruction per clock
Superscalar processor 超标量处理器:
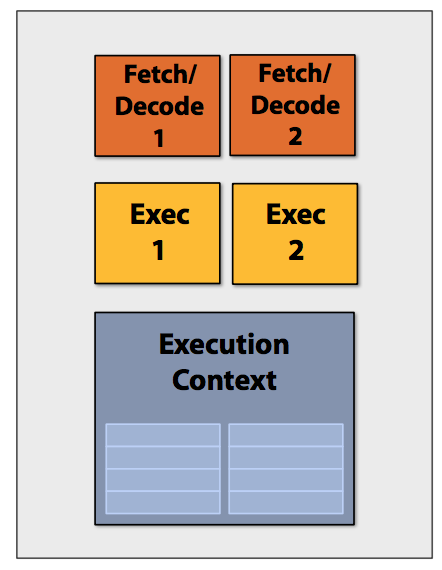
Decode*2, ALU*2, can run two instructions same time(if dependent)
加速:
- 单核芯片通过增减transistor来增减运行instruction的速度,more transistors = hold more data = large cache
- multiple core(each core is slower than simple core adding transistors)
- change program by using pthread to achieve parallisum
- change program by using data parallel expression
SIMD Processing
SIMD: single instruction, multiple data
Basic idea: adding ALUs to increase compute capability
Explicit SIMD”: SIMD parallelization is performed at compile time
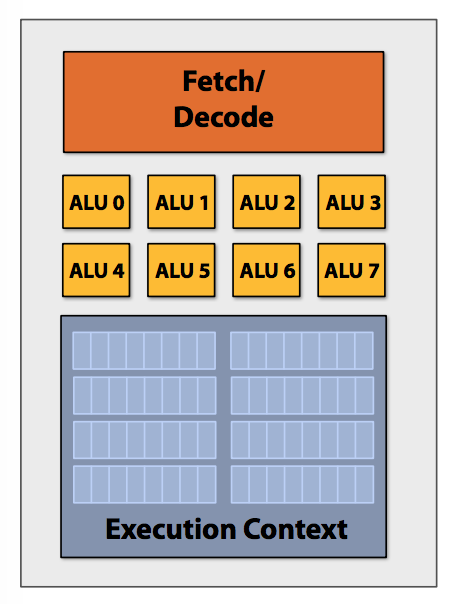
- Hardware (not compiler) is responsible for simultaneously executing the sameinstruction from multiple instances on different data on SIMD ALUs
- With one decode and multiple ALU, simply broadcast instruction to all ALUs and execute on all ALUs in parallel
对于example code相当于同时对于cache中的array,同时运行相同的程序,calculate by vector (HW1的vector算法很tricky表示并想不出来∠( ᐛ 」∠)_
Vector program(width=8):
void sinx(int N, int terms, float* x, float* result)
{
float three_fact = 6; // 3!
for (int i=0; i<N; i+=8) // calculate by vector, width=8
{
__m256 origx = _mm256_load_ps(&x[i]);
__m256 value = origx;
__m256 numer = _mm256_mul_ps(origx, _mm256_mul_ps(origx, origx));
__m256 denom = _mm256_set1ps(three_fact);
float sign = -1;
for (int j=1; j<=terms; j++)
{
// value += sign * numer / denom
__m256 tmp = _mm256_div_ps(_mm256_mul_ps(_mm256_set1ps(sign), numer), denom);
value = _mm256_add_ps(value, tmp);
numer = _mm256_mul_ps(numer, _mm256_mul_ps(origx, origx));
denom = _mm256_mul_ps(denom, _mm256_set1ps((2*j+2) * (2*j+3)));
sign *= -1;
}
_mm256_store_ps(&result[i], value);
}
}
SIMD applies same instruction to all elements simultaneously. So coherent execution is necessary for processing resources.
Possible bottleneck: divergent execution
也就是说对于vector中的每一个element,SIMD要求执行相同的指令。所以当遇到if condition的时候会造成资源的浪费。
Condition: mask of ALU
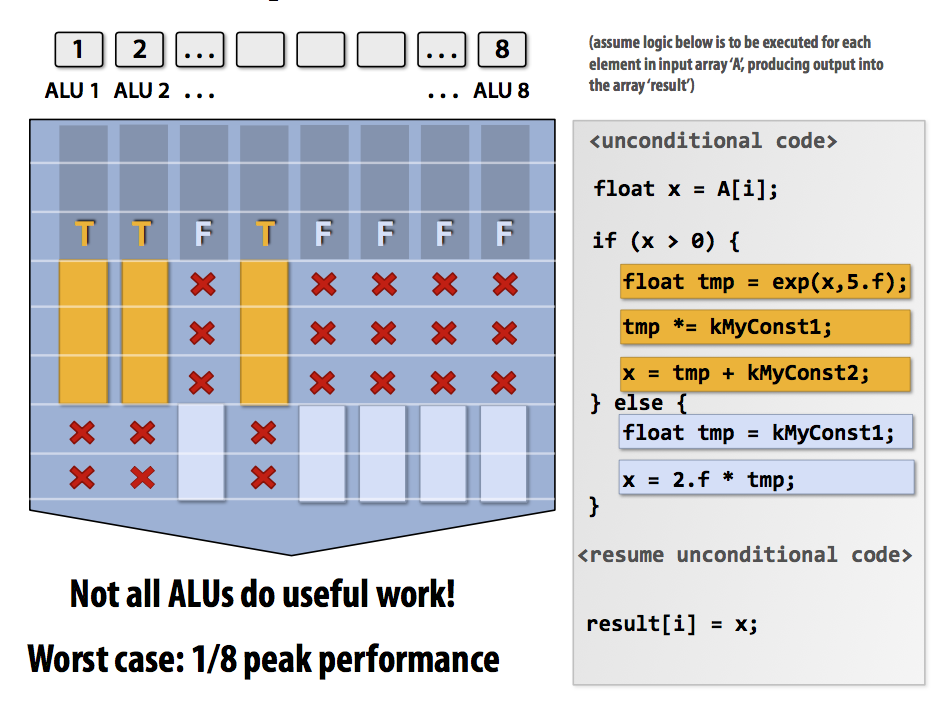
Worst case: 1/8 peak performance
Solution: change program to reach full performance
三种Parallel Execution对比:
- Multi-core 多核:multiple processing core
- thread level parallelism:simultaneously execute different instrection stream on each core
- SW decides to create threads (by pthreads)
- SIMD: multiple ALU
- vectorization done by complier(explicit SIMD) or at runtion by HW
- dependencies known prior to execution
- Superscalar: instruction level parallelism (ILP) on one core
- parallel by HW during execution
Accessing memory
访问内存的效率会对程序的整体效率产生很大的影响。(hw2循环里疯狂访问,笑
Memory latency 延迟:The amount of time for a memory request (e.g., load, store) from aprocessor to be serviced by the memory system
Memory bandwidth 带宽: The rate at which the memory system can provide data to a processor
Stalls 停顿: A processor “stalls” when it cannot run the next instruction in an instruction stream because of a dependency on a previous instruction
不知道多少天之后…
感觉就算写出来自己以后也不会看毕竟用进废退之后也不会再写mpi/omp相关的东西选PP也就是充值信仰(不是)那我还总结什么呢反正也没人会看的哇所以也就是强迫症不允许我写一半吧∠( ᐛ 」∠)_ 呸,不复习一下要是忘了怎么办啊?肯定会忘的,都会忘的ಥ_ಥ。
- Caches reduce memory access latency(reduce length of stalls)
- Prefetching reduces stalls (hide latency)
- Multi-threading reduces stalls
多线程能够隐藏停顿:在某个thread因为依赖等原因处于停顿状态时运行其他thread,因此能够提升整体的吞吐量但是对于某个thread运行时间增加。
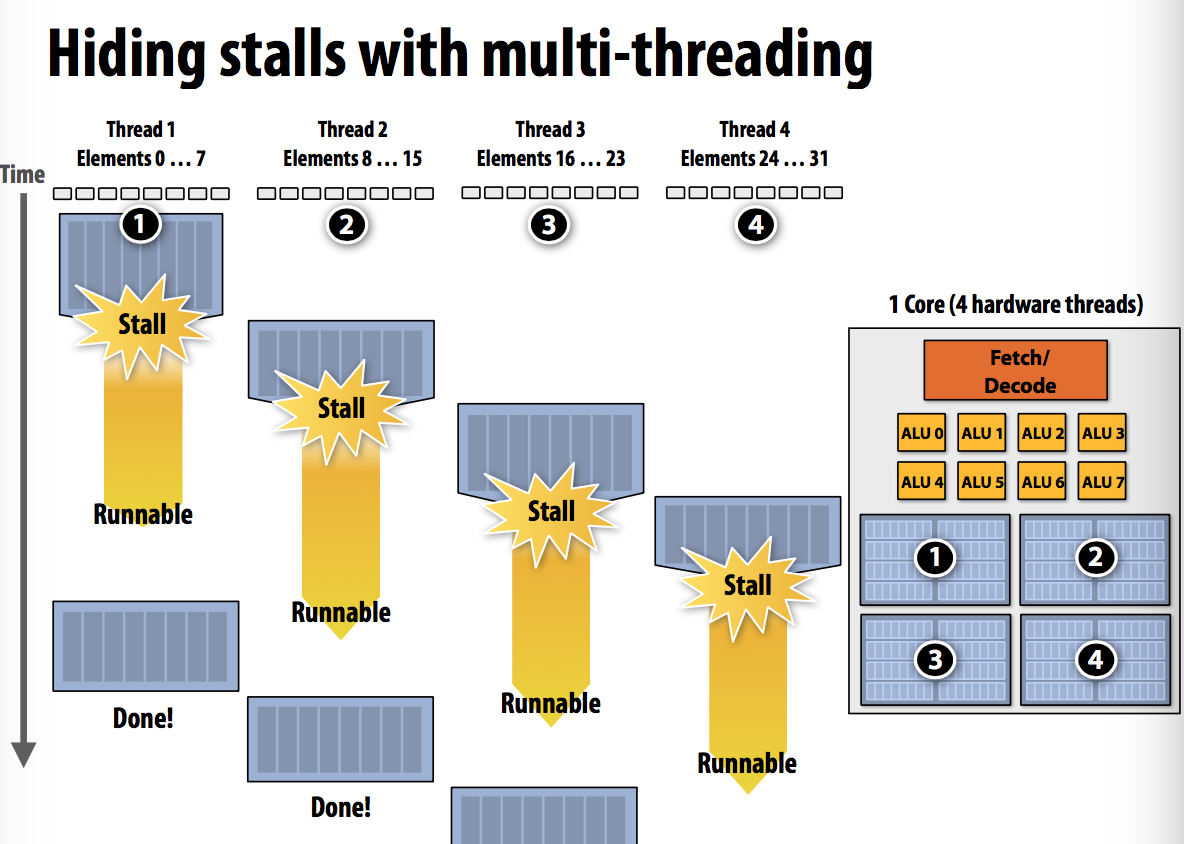
Hardware-supported multi-threading
- Core manages execution contexts for multiple threads -> more core
- Interleaved multi-threading -> more ALU
- Simultaneous multi-threading -> more state
- OS is responsible for mapping your pthreads to the processor’s thread execution contexts
Multi-threading summary
- Benefit: use core’s ALU resources more efficienctly
- hide memory latency
- fill multiple functional units of superscalar architecture
- Costs
- additional storage for thread context
- increases run time of any single thread
- additional independent work in a program
- relies heavily on memory bandwidth
随手看一眼CPU和GPU的区别:
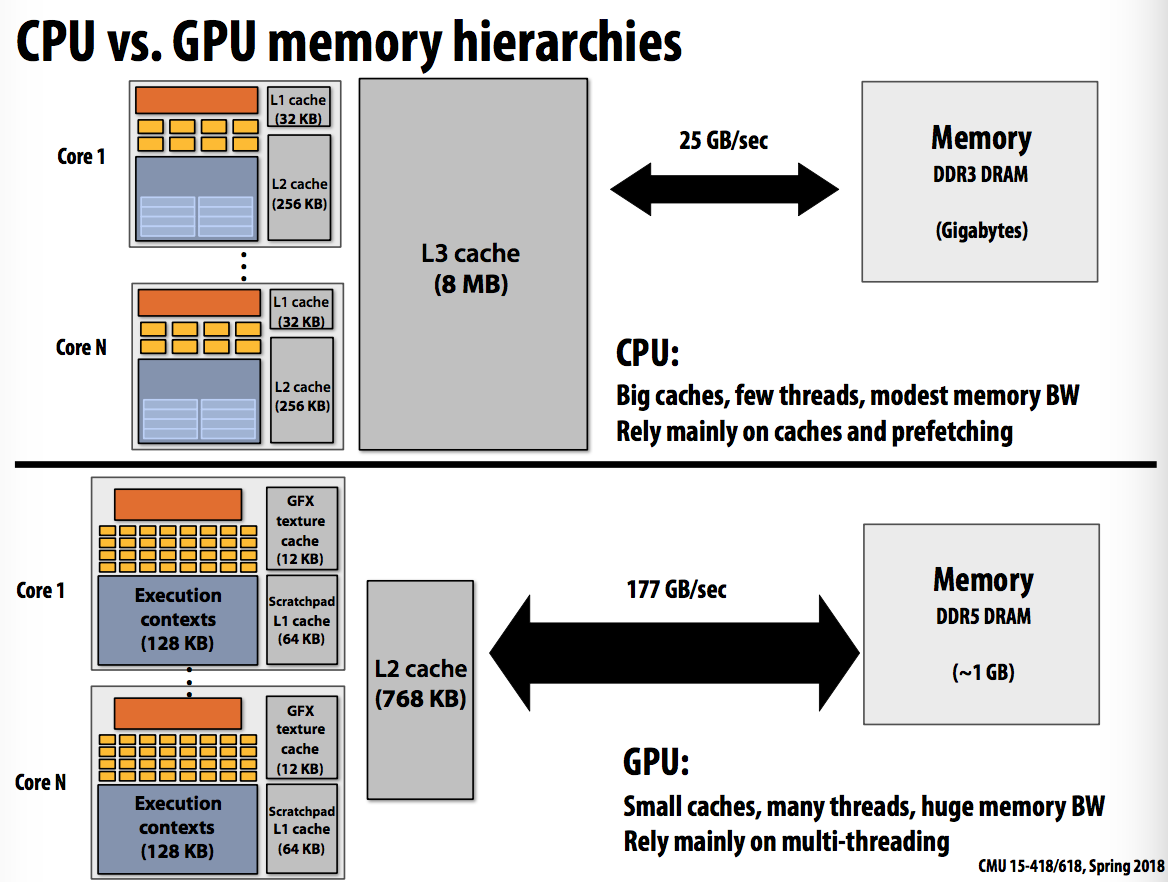
….内心复杂
- GPU architectures use the same throughput computing ideas as CPUs: but GPUs push these concepts to extreme scales
Bandwidth limited
Due to high arithmetic capability on modern chips, many parallel applications (on both CPUs and GPUs) are bandwidth bound
Performant parallel programs:
- Organize computation to fetch data from memory less often
- Request data less often
Summary
嗯这节课介绍处理器提升performance的主要方式:
- 多核 - simple cores
- SIMD - instruction stream over ALUs
- 多线程 - hide latency
然后举例几种parallel的方式:
- Superscalar processor (超标量处理机?
- executes more than one instruction per clock from a single instruction stream
- Multiple cores 多核
- executes one instruction per clock from an instruction stream on each core (multiple cores simultaneously)
- SIMD (single instruction multiple data)
- share instruction stream across execution of multiple iterations
都放在一起就:
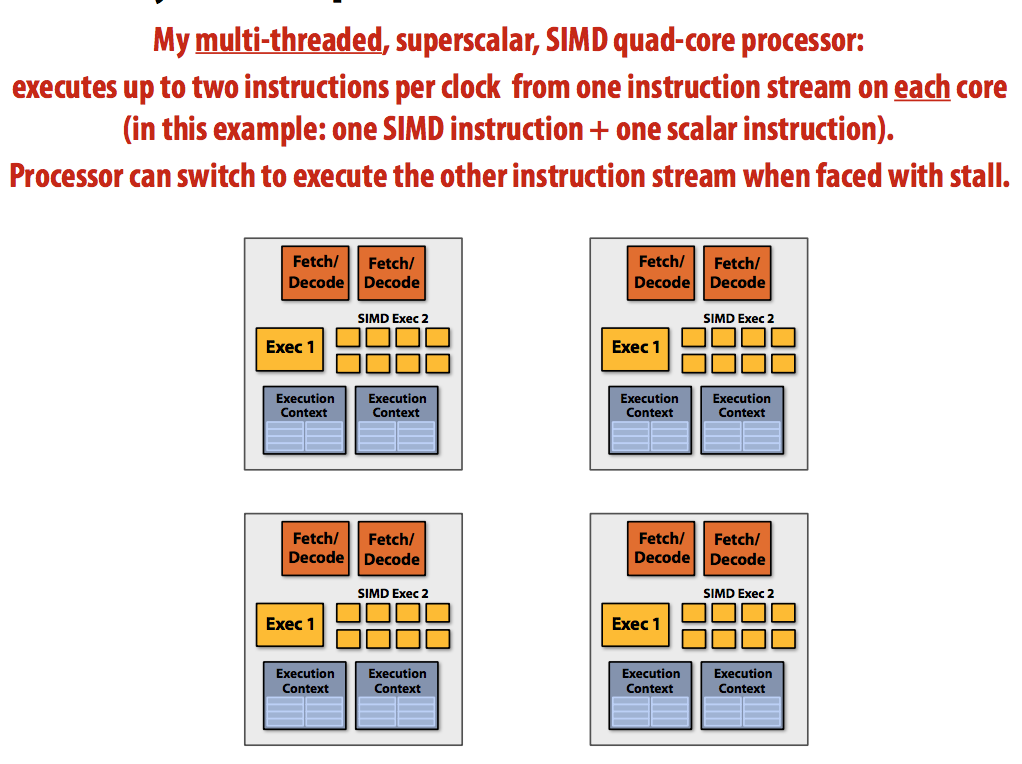
从一开始,这课让我觉得自己是智障∠( ᐛ 」∠)_ (后来更证明了这个想法
“Running in circles
Coming in tails
Heads are a science apart”