Parallel Architecture & Programing 肆
过了好几个月,经过了好多我也不知道有什么用的Data乱实验,买了PS4和switch,感觉玩游戏也没有很有意思。2019年了希望可以好好生活吧 :) 我嘴上说着佛系活着,可还是会日常一不小心自闭了。同样都是人,我怎么就丧丧丧呢_(´ཀ`」 ∠)_ 不写完怪难受的,继续自娱自乐。
CUDA和GPU可以说是经常接触到了,虽然我无需再写cuda代码。但是我拿cuda文档和gpu结构当头像因为它们好看。
Background
一些如果不知道就会非常迷茫的概念:
-
CPU: A central processor unit
- GPU: A graphics processing unit
- Host: The “normal computer” GPU connected
- Device: GPU and its memory
- CUDA: Compute Unified Device Architecture
- OpenCL: Open Computing Language
之前简单介绍了CPU的结构。在多核CPU上跑程序,OS将程序载入内存,选择execution context(执行上下文), 准备寄存器等等,处理器在执行上下文维持的环境下执行指令。 提到寄存器两开花:
- Registers are the smallest and the fastest storage unit(s) a CPU which stores instructions await to be decoded or executed.
- PC - program counter 程序计数器- stores address of the -> next <- instruction in RAM
- MAR - memory address register 地址寄存器
- MDR - memory data register 数据寄存器 - stores the data that is to be sent to or fetched from memory
- CIR - current instruction register 指令寄存器 - stores actual instruction that is being decoded and executed
- ACC - accumulator 累加寄存器- stores result of calculations
- IR - interrupt register 中断寄存器 - manages requests from I/O devices
CUDA
2007年NVIDIA发布CUDA,一种跑在GPU上长得有点像C的编程模型。Design goal: maintain low abstraction distance. 就写个笔记写一晚上QAQ,来不及去gym了。
相关概念:
-
Host 主机端 :一般是CPU
- Device 设备端:GPU
- Global memory:Device memory shared across various blocks
- CUDAMalloc(), CUDAMemcpy(), CUDAFree()
- Shared memory: Memory shared only by threads within associated block
- __shared__
- Kernel: The work to be parallelized across GPU’s cores
- Thread: An abstraction for work associated with an instance of kernel
- Block: Thread block, a partition threads be dispatched to a GPU
- Grid 网格: Set of all blocks
- CUDA Core: A single graphics process core
- Streaming Multiprocessor: A collection of CUDA Cores architected together to form a single GPU. Threads within a thread block concurrently execute on an SM.
-
Warp 线程束: A division of a block created within the SM to assign work to cores. Warps aren’t schedule until a core is available for each thread within the warp.
- __shared__: Qualifier to declare a variable in shared (per thread block) memory
- __global__: Qualifier to place a function into device memory, for execution onto the device, but enabling it to be callable from the host
CUDA memory model
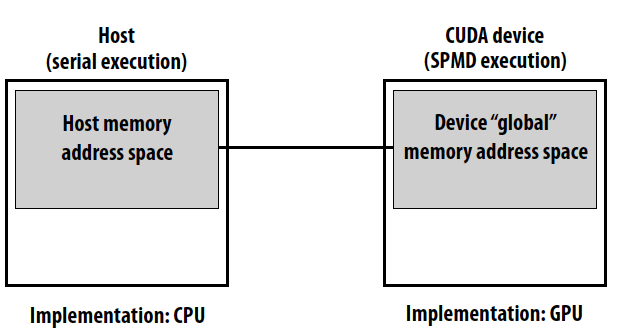
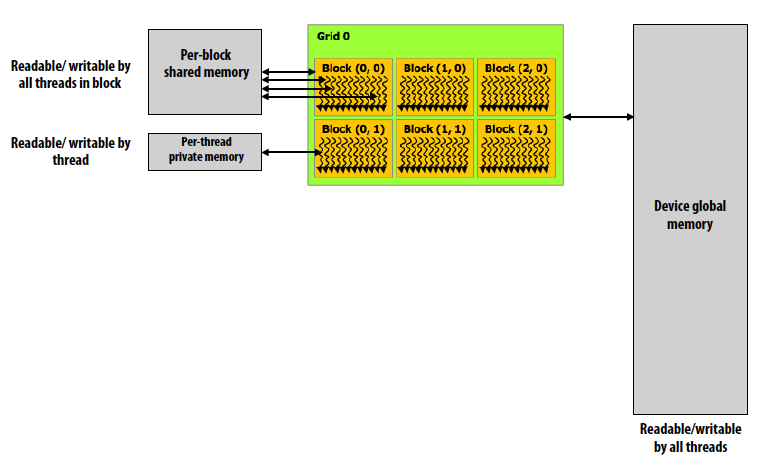
CUDA语法分为两个部分,host code和CUDA device code。Host部分运行在CPU上, 采用Serial execution,如同普通的C代码应用,当所有的CUDA threads结束时返回。CUDA device部分运行在GPU上,采用SPMD(Single Program Multiple Data) execution,kernel(__global__)是每个threads并行执行的函数,每个thread通过threadIdInBlock和blockIdInGrid计算出grid里的唯一threadId,这个CUDA Thread Indexing Cheatsheet清楚展示了threadId的计算。我的Assign2由于算错线程号而改了好半天最后还是HarryTA发现了错误。
- Major CUDA assumption: Thread block execution can be carried out in any order
- GPU implementation maps thread blocks to cores using a dynamic scheduling policy that respects resource requirements
CUDA 层次结构
A kernel is launched as a grid of blocks of threads
一个kernel函数运行的所有线程为一个grid,grid分为很多thread of block,每个block里有很多线程。通过built-in变量threadIdx, blockIdx, blockDim, gridDim等可以找到每个thread在grid里的特有id。线程IDs最高可以是3维的。
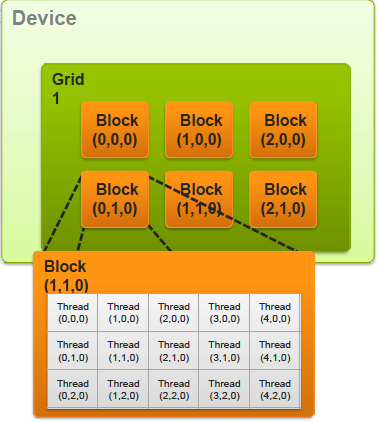
Thread blocks在系统中毫无依赖关系,可以以任何顺序调度,同一个block中的threads并行运行,可以看作一个SPMD程序。一个thread block上的线程在同一个GPU核上执行,它们可以通过shared memory来快速通信。在GPU硬件上,线程被分为warp,采用SIMD执行。
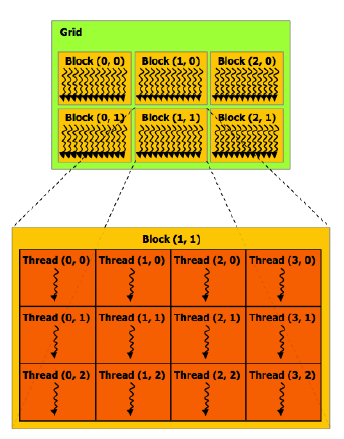
举一个矩阵运算的例子,假设block是2维的,那么有两种data access的方式:

- CUDA threads numbered within block in row-major order
- Threads with same value of Yand consecutive values of Xmap to consecutive positions in single warp
- When single warp accesses consecutive memory locations, do block read or write
- When single warp accesses separated memory locations, requires gather(read) or scatter(write)
对于这段device代码
float sum = 0.0;
for ( int k = 0; < N; k++) {
sum += dmatA[RM(i,k,N)] * dmatB [RM( k,j,N )];
}
dmatC [RM(i,j,N)] = sum;
Regular方式中一个warp中的thread具有相同的i和k,以及连续的j,warp的读写符合memory organization。Inverted方式中一个warp中的thread具有相同的k和j,以及连续的i,warp的读写不符合memory organization,因为存在多个warp访问相同内存的情况。
Warp
- A warp is a CUDA implementation detail on NVIDIA GPUs
- On modern NVIDIA hardware, groups of 32 CUDA threads in a thread block are executed simultaneously using 32-wide SIMD execution
- The group of 32 threads sharing an instruction stream is called a warp
32个共享指令流的CUDA线程叫做一个Warp,这些线程执行相同的指令,但是有可能会进入不同的分支,此时performance会下降。在一个thread block中,0-31号threads在同一个warp中,以此类推。因为warp采用32-wide SIMD架构,block size一般为32的倍数。
Synchronization constructs
- __syncthreads()__: Barrier to ensure all threads get there before any continue
- Atomic operations: On both global memory and shared memory variables
- Host/device sync: Implicit barrier across all threads at return of kernel
Reference
CUDA Thread Indexing Cheatsheet
CUDA gdb 我debug的巨差无比
CUDA编程入门极简教程 这个写的好清楚(//∇//)!