Parallel Architecture & Programing 柒
真是令人自闭的一天呀, 晚上继续复习PP玩耍。快要过年了,希望新的一年能够成为成为更好的自己吧。或许我该勇敢一些,反正也没什么好失去的不是吗。游戏机卖不出去了
Interconnect Network
Interconnection Network 互联网络
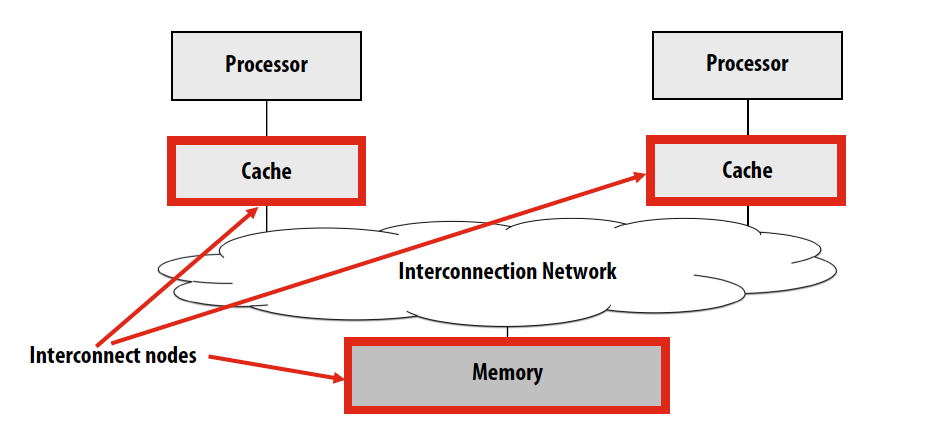
- Used for connecting:
- Processor cores with other cores/memories/caches
- Caches and caches
- I/O devices
- Importance:
- For system scalability
- For system performance and energy efficiency
Terminology
-
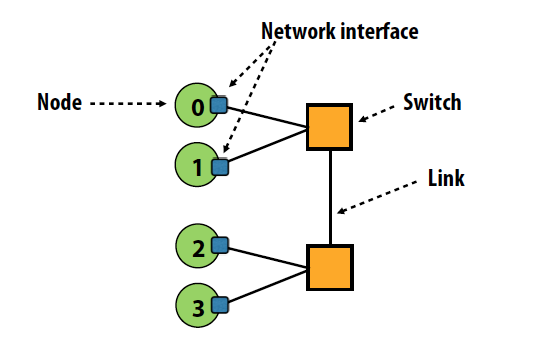
Network node: A network endpoint connected to a router/switch
-
Network interface: Connects nodes to the network
- Switch/router: Connects a fixed number of input links to a fixed number of output links
- Link: A bundle of wires carrying a signal
- Topology 拓扑结构: How switches are connected via links
- Routing 路由: How a message gets from its source to its destination in the network
- Buffering and flow control
Properties of interconnect topology
- Routing distance: Number of links (“hops”) along a route between two nodes
-
Diameter: the maximum routing distance
-
Average distance: average routing distance over all valid routes
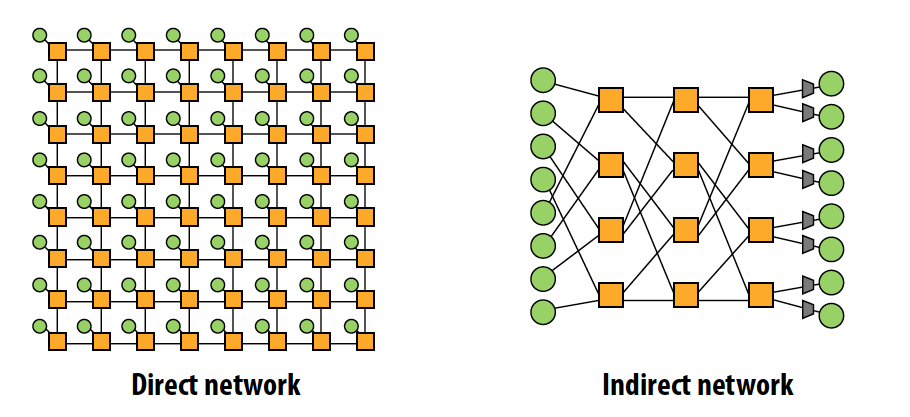
- Direct 直接 vs. Indirect 间接 networks
- Direct network: endpoints sit “inside” the network
-
Bisection bandwidth:Cut network in half, sum bandwidth of all severed links
-
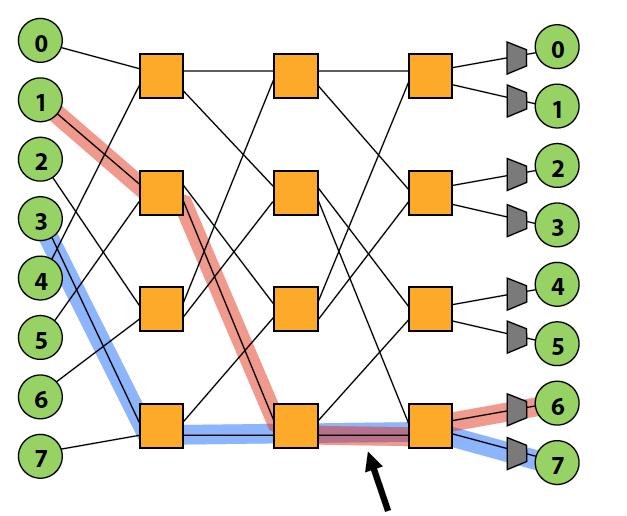
Blocking 阻塞 vs. Non-blocking 非阻塞
- If connecting any pairing of nodes is possible, network is non-blocking (otherwise, it’s blocking)
一个block的例子,存在资源的竞争:
Interconnect topologies
Bus interconnect
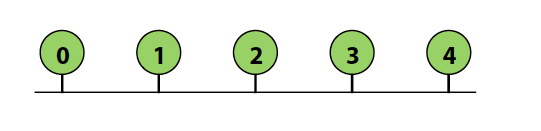
- Good:
- Simple design, easy to implement coherence (via snooping)
- Cost effective for a small number of nodes
- Bad:
- Contention: all nodes contend for shared bus
- Limited bandwidth: all nodes communicate over same wires(1 per time)
- High electrical load = low frequency, high power
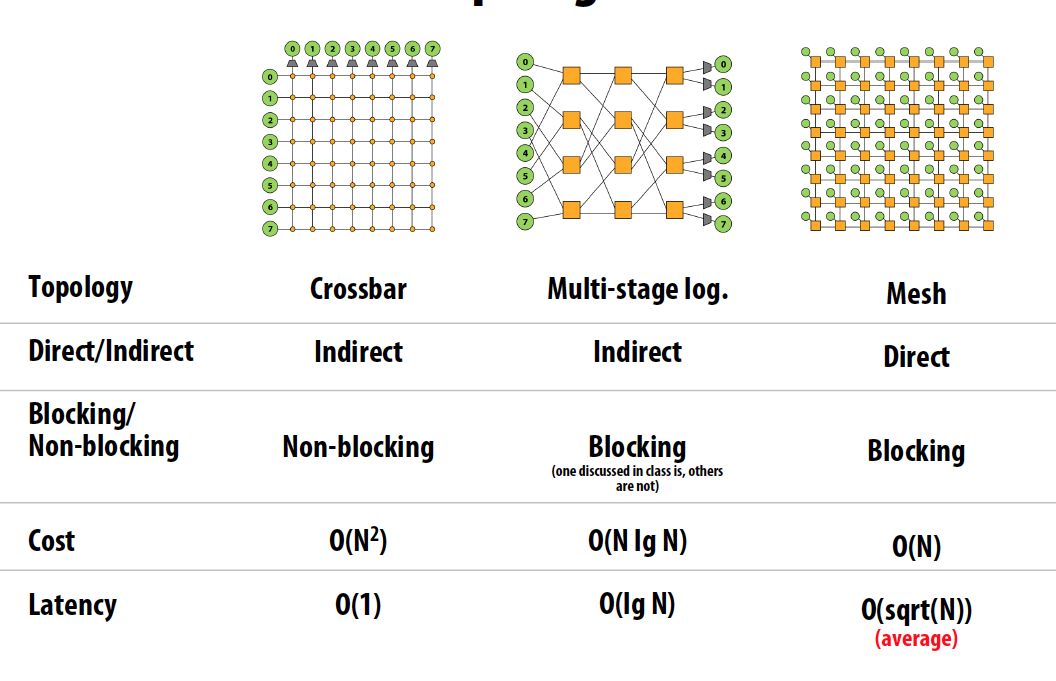
Crossbar interconnect
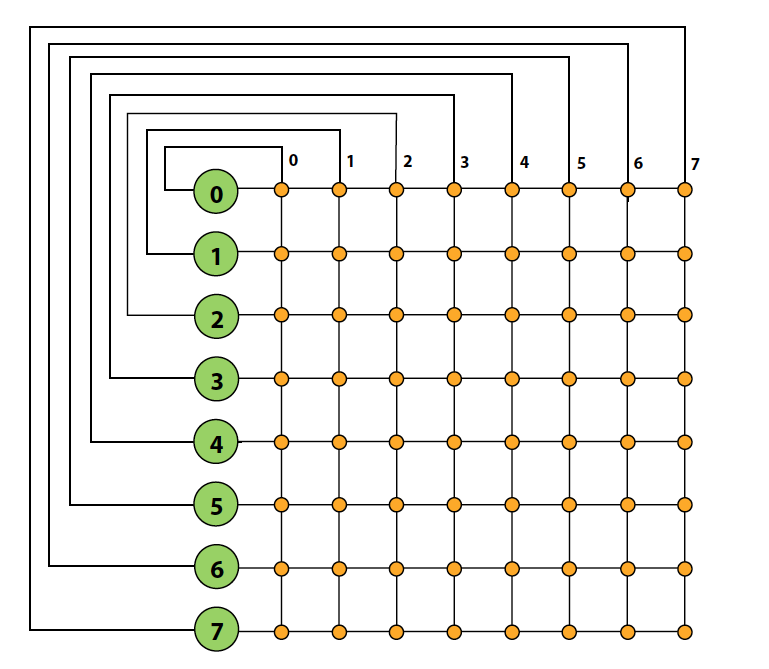
- Every node is connected to every other node (non-blocking, indirect)
- Good: O(1) latency and high bandwidth
- Bad:
- Not scalable: O(N2) switches
- High cost
- Difficult to arbitrate at scale
Ring
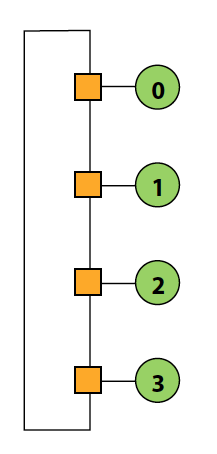
- Good:
- Simple
- Cheap: O(N) cost
-
Bad:
-
High latency: O(N)
-
Bisection bandwidth remains constant as nodes are added (scalability issue)
-
Mesh
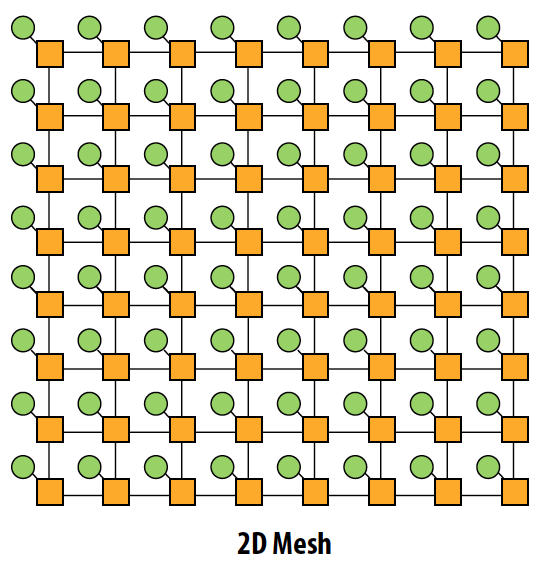
- Direct network
- O(N) cost, average latency: O(sqrt(N))
- Path diversity: many ways for message to travel from one node to another
Torus
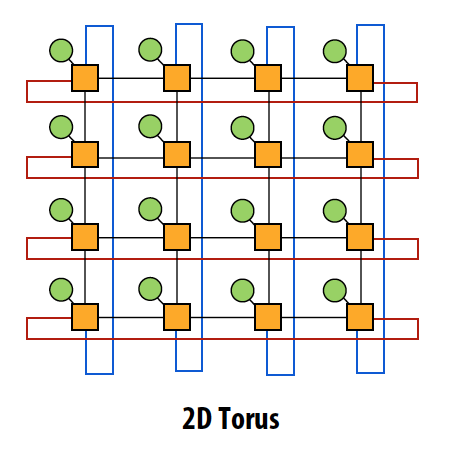
- O(N) cost, but higher cost than 2D grid
- Higher path diversity and bisection BW than mesh
- Higher complexity
- Characteristics of mesh topology are different based on whether node is near edge or middle of network
Trees
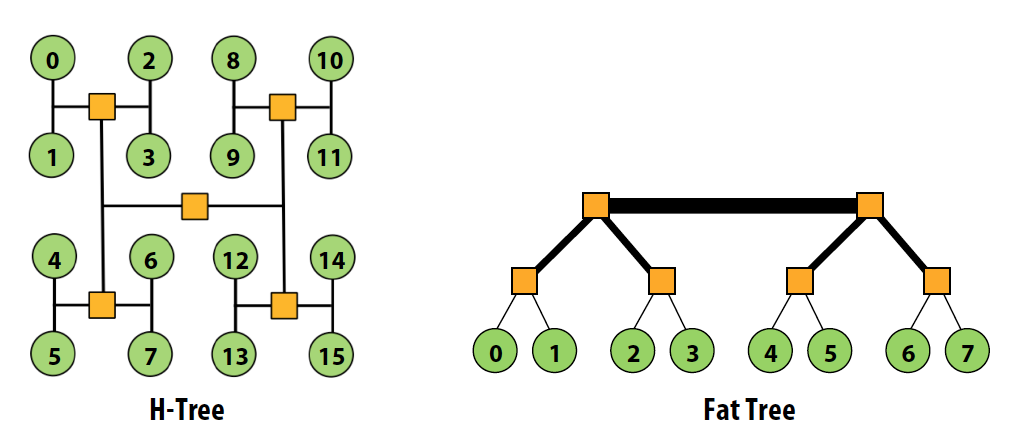
我想起来了,这个胖树,胖。。。QAQ
- Planar, hierarchical topology
- Like mesh/torus, good when traffic has locality
- Latency: O(lg N)
- Use “fat trees”(higher bandwidth links near root) to alleviate root bandwidth problem
- O(N) bisection bandwidth
- Routing: like tree routing, but randomly choose when multiple links possible
Multi-stage logarithmic Routing
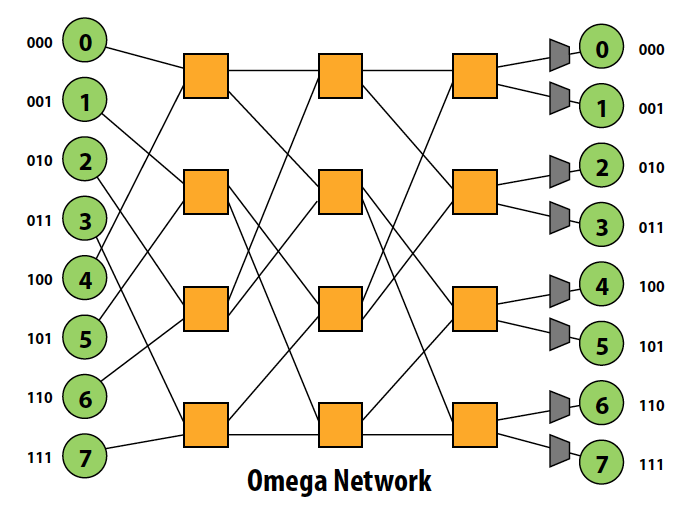
- Indirect network with multiple switches between terminals
- Cost O(N lg N), latency O(lg N)
Buffering and flow control
我想不通我当时是怎么看不明白这课件的?失去智力吗_(:з」∠)_ 真是脑子是好的希望我也有?
Circuit switching 电路交换 vs. packet switching 封包交换
- Circuit switching sets up a full path between sender and receiver prior to sending a message
- Establish route (reserve links) then send all data for message
- Higher bandwidth transmission (no per-packet link mgmt overhead)
- Does incur overhead to set up/tear down path
- Reserving links can result in low utilization
- Packet switching makes routing decisions per packet
- Route each packet individually (possibly over different network links)
- Opportunity to use link for a packet whenever link is idle
- Overhead due to dynamic switching logic during transmission
- No setup/tear down overhead
Granularity of communication
- Message
- Unit of transfer between network clients
- Can be transmitted using many packets
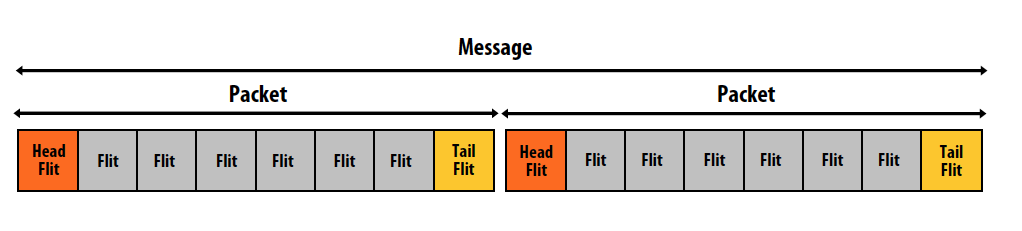
- Packet
- Unit of transfer for network
- Can be transmitted using multiple flits
- Format:
- Header: Contains routing and control information
- Payload/body: containing the data to be sent
- Tail: Contains control information
- Flit (flow control digit)
- Packets broken into smaller units called “flits”
- Flit: (“flow control digit”) a unit of flow control in the network
- Flits become minimum granularity of routing/buffering
Flow control
都是概念我是怎么做到不会的呢ORZ。。。
Circuit-switched routing
- High-granularity resource allocation
- Pre-allocate all resources (links across multiple switches) along entire network path for a message
- Cost
- Needs setup phase (“probe”) to set up the path
- Lower link utilization. Transmission of two messages cannot share same link
- Benefits
- No contention during transmission due to preallocation, so no need for buffering
- Arbitrary message sizes
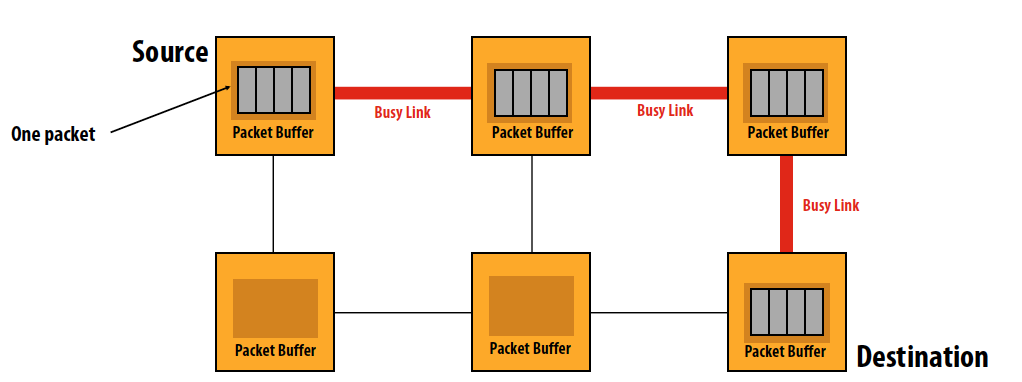
Store-and-forward (packet-based routing)
- Packet copied entirely into network switch before moving to next node
- Flow control unit is an entire packet
- Requires buffering for entire packet in each router
- High per-packet latency (latency = packet transmission time on link * network distance)
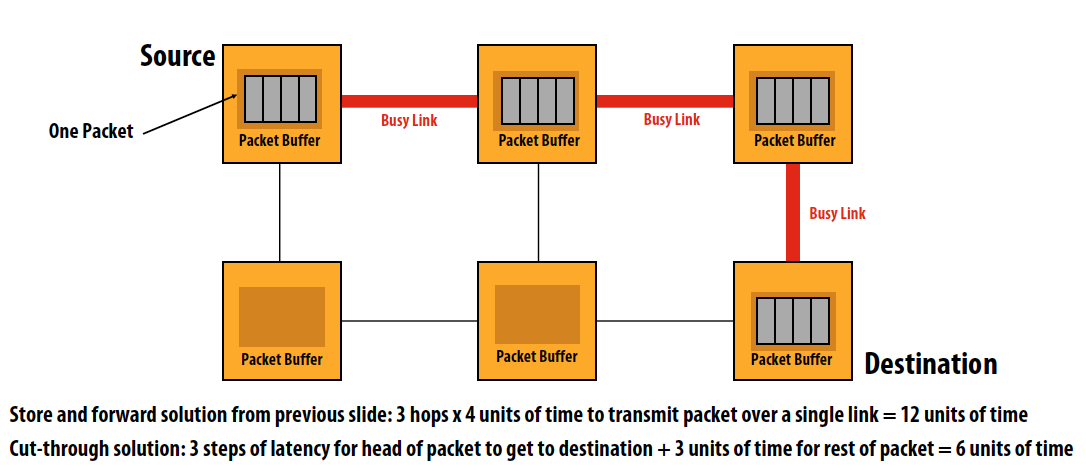
Cut-through flow control (also packet-based)
- Switch starts forwarding data on next link as soon as packet header is received
- Result: reduced transmission latency
- If output link is blocked (cannot transmit head), transmission of tail can continue
- Worst case: entire message is absorbed into a buffer in a switch
- Requires switches to have buffering for entire packet, just like store-and-forward
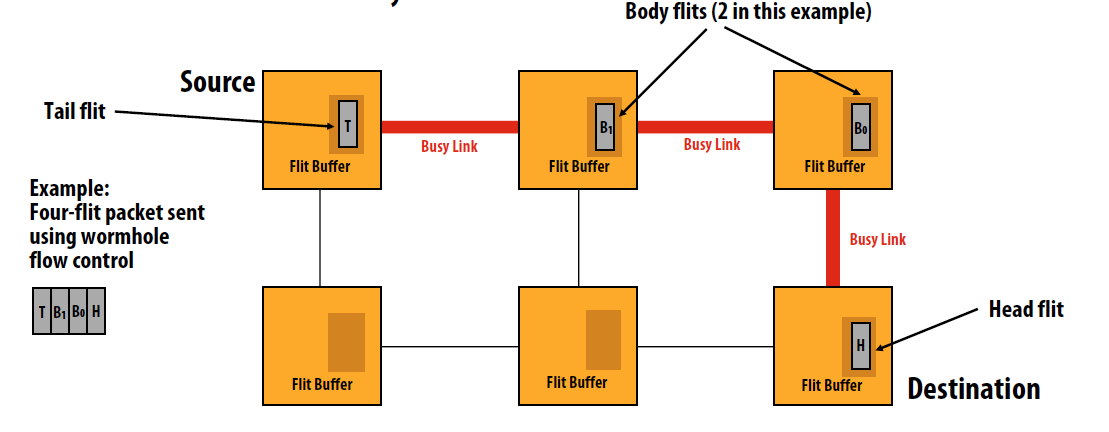
Wormhole flow control
- Flit: Packets broken into smaller units called “flits”
- Routing information only in head flit
- Body flits follows head, tail flit flows body
- If head flit blocks, rest of packet stops
- Completely pipelined transmission
- For long messages, latency is almost entirely independent of network distance (pipeline)
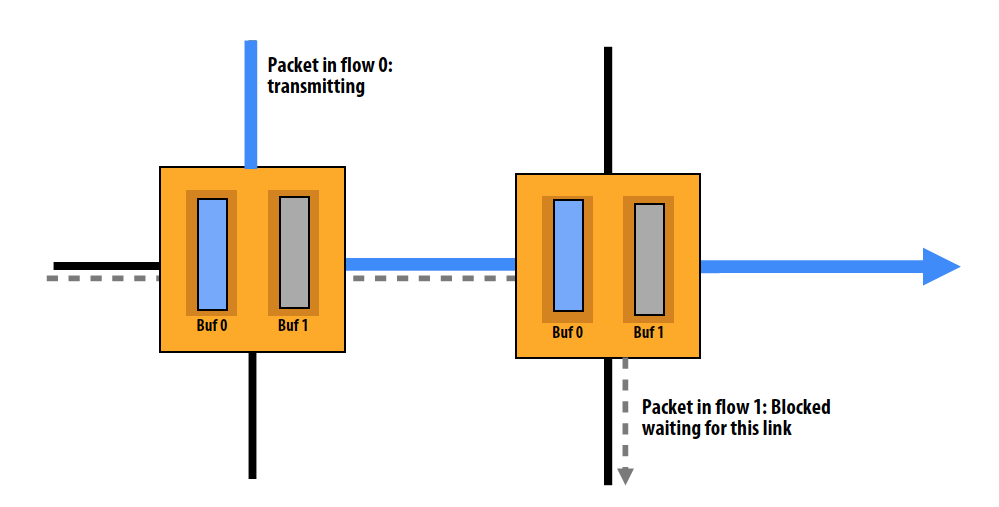
Virtual channel flow control
- Multiplex multiple operations over single physical channel
- Divide switch’s input buffer into multiple buffers sharing a single physical channel
- Reduces head-of-line blocking
- Other uses:
- Deadlock avoidance
- Prioritization of traffic classes
这次的都是些概念,复杂度也很好算。我知道复习这些一点用都没有,但是还是想完成,因为该死的仪式感和整体感。马上过年了,支付宝集个福蛮有气氛,挺好。