Parallel Architecture & Programing 贰
本来打算放弃写笔记了不过最近因为学妹住到家里又想起了CMU生涯,捡起之前的笔记看看,一个挣扎着起来的垃圾。
并行编程的基础知识,包括抽象和实现的区分,几种常用的并发编程模型及其应用,识别依赖。
Abstraction Vs. Implementation
之前不太能分清上层抽象和下层实现的关系_(:з」∠)_
举个ISPC(Intel SPMD Programing Complier)的例子。ISPC code:
export void sinx(
uniform int N,
uniform int terms,
uniform float* x,
uniform float* result)
{
// assume N % programCount = 0
for (uniform int i=0; i<N; i+=programCount)
{
int idx = i + programIndex;
float value = x[idx];
float numer = x[idx] * x[idx] * x[idx];
uniform int denom = 6; // 3!
uniform int sign = -1;
for (uniform int j=1; j<=terms; j++)
{
value += sign * numer / denom
numer *= x[idx] * x[idx];
denom *= (2*j+2) * (2*j+3);
sign *= -1;
}
result[idx] = value;
}
}
- SPMD programing abstraction: call to ISPC function spawns “gang” of ISPC “program instances”, all instances run ISPC code concurrently, upon return, all instances have complete
- ISPC compiler generates SIMD implementation: number of instances in a gang is the SIMD width of the hardware, ISPC compiler generates binary with SIMD instructions, C++ code links against object files
上层抽象和具体实现没关系,我内心复杂和Parallel也没关系∠( ᐛ 」∠)_
感觉Abstracion明确了程序功能的实现,具体如何使其实现的硬件Implementation可以有很多种方法呢
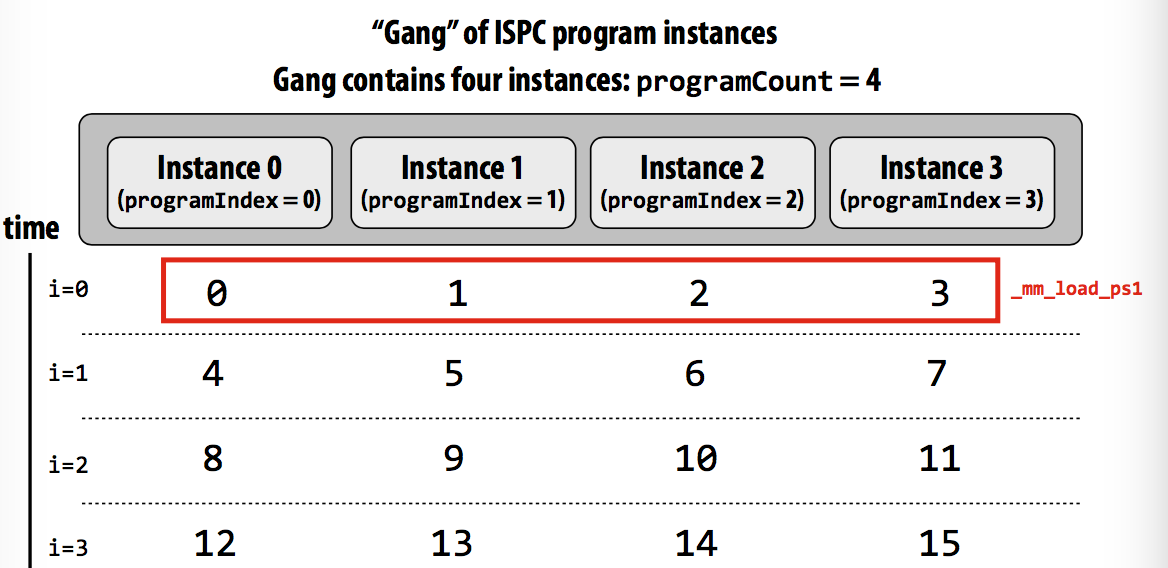
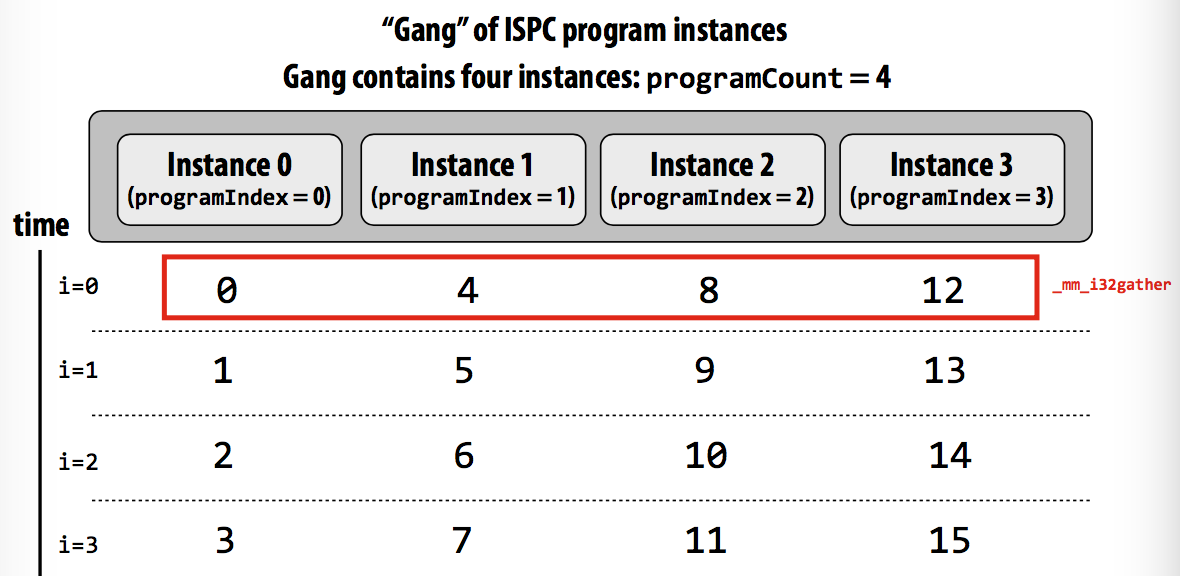
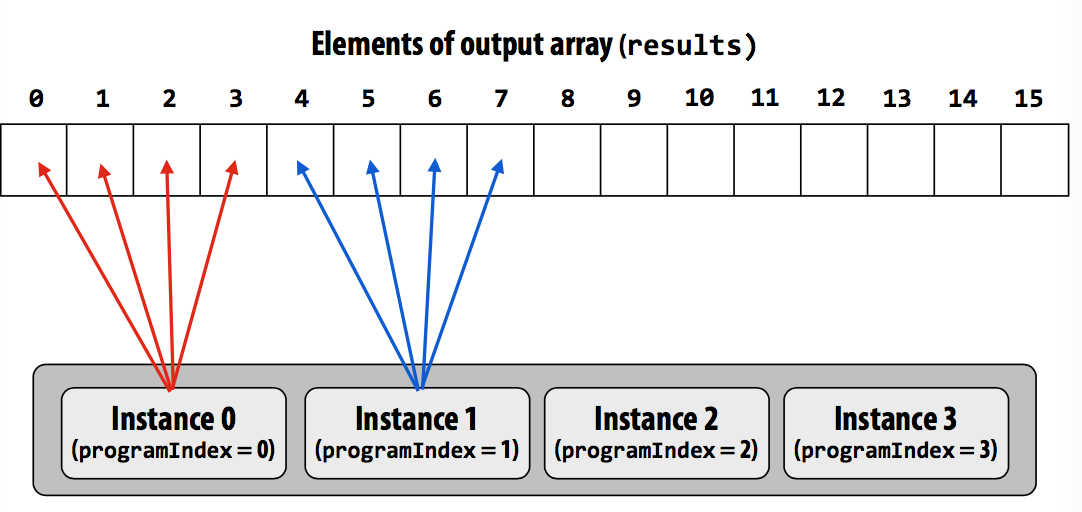
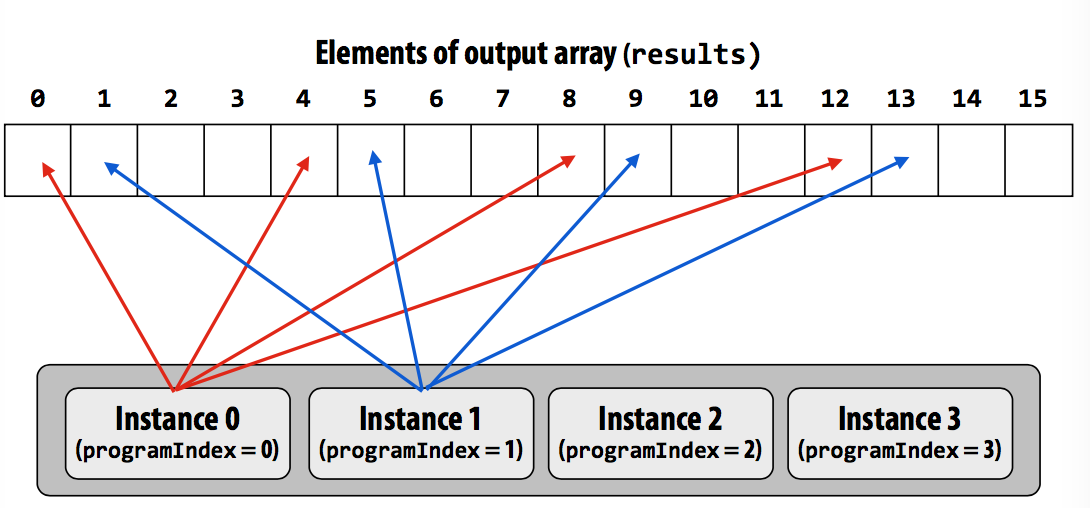
Two ways program instances loop iterations:
-
Interleaved assignment (交错?
For all program instances, the four values are contiguous in memory
-
Blocked assignment (列块?
Touches four non-contiguous values in memory.
Need “gather” instruction to implement.
| Interleaved | Blocked |
|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Interleaved分配方式在instance中连续的数据存在连续的内存中。
Three parallel programing model
Shared address space
共享地址空间模型(抽象.jpg), 所有的线程可以读写共享变量
- Threads communicate by reading/writing to shared variables
- Threads manipulate synchronization primitives: locks, semaphors, etc
- Logical extension of uniprocessor programming
Impementation: e.g. Non-uniform memory access(NUMA)
(所有processor可以存取任何地址,成本较高
Message passing
- Threads operate own private address spaces
- Threads communicate by sending/receiving message (想写go语言了_(:з」∠)_
Data parallel
- Map a function onto a large colleciton of data
- Often takes form of SPMD programming
- Related to Stream programing model
- Gather/Scatter communication primitive
实际应用常常3种模式混用。Typora的bug似乎有点多
等我再打开这个文件都快过了2个月了,我在干嘛呀orz 这篇不知道在干嘛就这样吧反正连我自己都不会再看了emmmmmm工作了这么久果然还是比上学时代轻松多了虽然自己菜。实在没想到现在从事的东西和我最耗尽心力的dspp一点关系都没得。想想其实自己也没有讨厌ml,也没有多热爱system。果然还是…呃,果然还是失礼了。要是我不菜也不蠢就好了。学习了学习了,学习使我快乐
Update10/10 到底在写什么鬼玩意
Speedup and Dependency
For a fix computation: Speedup(P processors) = Time(1 processor)/Time(P processors)
Amdahl’s law: dependencies limit maximum speedup due to parallelism
aka S = inherently sequential fraction of execution, maximum speed up <=
For p processors, max speed up <=
Decomposition
- breakup to tasks can be carried out in parallel
- identifying dependencies
- programmer responsible
Assignment
- balance workload, reduce communication costs
- statically or dynamically during execution
- languages/runtimes responsible
Orchestration
- reduce costs of communication/sync, preserve locality, reduce overhead
Mapping to hardware
- mapping threads to hardware execution units